Tag Archives: STR()
xBase File Types
xBase File Types and Extensions
| Ext. | File Type | Introduced or used by |
| .$$$ | temporary file | dBASE III |
| .$db | temporary file | dBASE IV |
| .act | FoxDoc Action Diagrams | FoxPro |
| .app | application object file | dBASE Appl. Generator |
| .app | generated application | FoxPro |
| .bak | Backup file | dBASE |
| .bar | horizontal bar menu object file | dBASE Appl. Generator |
| .bin | Binary files | dBASE |
| .bch | batch process object file | dBASE Appl. Generator |
| .cac | executable when caching on/off | dBASE IV |
| .cat | catalog | dBASE III, IV |
| .cdx | compound index | FoxPro |
| .ch | header file | Clipper |
| .cht | interface file for ChartMaster | dBASE |
| .clp | compiler script file (clip list) | Clipper |
| .cmd | command | dBASE – Waffle |
| .cod | template source file | dBASE Appl. Generator |
| .cpt | encrypted memo file | dBASE |
| .crp | encrypted database | dBASE IV |
| .ctl | control file | dBASE IV – Aldus Setup |
| .cvt | backup file for CONVERTed database file | dBASE IV |
| .db | configuration | dBASE |
| .db$ | temporary file | dBASE |
| .db2 | database | dBASE II |
| .db3 | database | dBASE III |
| .dbf | database file | dBASE – FoxPro |
| .dbk | database backup | dBASE IV |
| .dbo | compiled program | dBASE IV |
| .dbt | FoxBASE+ style memo | FoxPro |
| .dbt | memo file for database w/same name | dBASE – Clipper |
| .def | Definitions list | dBASE |
| .dif | Data Interchange Format. For APPEND FROM, COPY | dBASE – VisiCal |
| .doc | Documentation text file | dBASE Appl. Generator |
| .fil | files list object file | dBASE Appl. Generator |
| .fky | macro file | FoxPro |
| .fmo | compiled format file | dBASE IV |
| .fmt | format file | dBASE – FoxPro – Clipper |
| .fp | configuration file | FoxPro |
| .fpc | catalog | FoxPro |
| .fpt | memo | FoxPro |
| .fr3 | renamed dBASE III+ form file | dBASE IV |
| .frg | uncompiled report file, code fragment file | dBASE IV |
| .frm | report file | dBASE – Clipper |
| .fro | compiled report file | dBASE IV |
| .frt | report memo | FoxPro |
| .frx | report | FoxPro |
| .fw2 | Framework spreadsheet or database file | Framework – dBASE |
| .fxp | compiled format | FoxPro |
| .gen | compiled template | dBASE Appl. Generator |
| .idx | index (many) | FoxPro |
| .ind | include index | dBASE IV |
| .inx | index | FoxBase |
| .key | Key macro library | dBASE |
| .lbg | label generator data | dBASE IV |
| .lbl | label | dBASE – Clipper |
| .lbo | compiled label | dBASE IV |
| .lbt | label memo | FoxPro |
| .lbx | label | FoxPro |
| .ld1 | overlay file | dBASE |
| .log | Transaction log file | dBASE |
| .mbk | multiple index file backup | dBASE IV |
| .mdx | multiple index file | dBASE IV |
| .mem | memory variable save file | dBASE – FoxPro |
| .mnt | menu memo | FoxPro |
| .mnx | menu | FoxPro |
| .mpr | generated program | FoxPro |
| .mpx | compiled menu program | FoxPro |
| .ndx | index file | dBASE |
| .npi | source for DGEN.EXE interpreter | dBASE Appl. Generator |
| .ntx | index file | Clipper |
| .pjt | project memo | FoxPro |
| .pjx | project | FoxPro |
| .plb | library | FoxPro |
| .pll | pre-linked library | Clipper |
| .plt | pre-linked transfer file | Clipper |
| .pop | pop-up menu object | dBASE Appl. Generator |
| .ppo | pre-processor output | Clipper |
| .pr2 | printer driver | dBASE IV |
| .pr3 | PostScript printer driver | dBASE IV |
| .prf | printer driver | dBASE IV |
| .prg | program source file | dBASE – FoxPro – Clipper |
| .prs | procedure | dBASE IV |
| .prt | Print dump | dBASE |
| .prx | compiled program | FoxPro |
| .qbe | saved query (Query By Example) | dBASE IV – Quattro Pro |
| .qbo | compiled query | dBASE IV |
| .qpr | generated query program | FoxPro |
| .qpx | compiled query program | FoxPro |
| .qry | query | dBASE IV |
| .res | dBASE resources | dBASE IV |
| .rpd | Rapid file. For IMPORT/EXPORT,APPEND FROM, COPY | dBASE |
| .sc3 | renamed dBASE III screen mask file | dBASE IV |
| .scr | screen – screen snapshot | dBASE IV |
| .sct | screen memo | FoxPro |
| .scx | screen | FoxPro |
| .spr | generated screen program | FoxPro |
| .spx | compiled screen program | FoxPro |
| .str | structure list object file | dBASE Appl. Generator |
| .t44 | Temporary file for Sort or Index | dBASE IV |
| .tbk | memo backup | dBASE IV – FoxPro |
| .tvf | table view settings | dBASE |
| .upd | update data | dBASE |
| .upo | compiled update data | dBASE |
| .val | values list object file | dBASE Appl. Generator |
| .vew | view file | Clipper, Lotus Approach |
| .vue | view | dBASE IV – FoxPro |
| .w44 | temporary file for Sort or Index | dBASE |
| .wfm | form object | dBASE Form Designer |
| .win | window file | FoxPro – dBASE |
Source : http://www.clicketyclick.dk/databases/xbase/format/index.html
Notes:
– Such a list can’t be perfect. Some item may be obsolete / forgotten and something may not exist when this list compiled.
– “Clipper” may not include all versions of Clipper.
– Most of Clipper files are supported by Harbour.
Hash Details – 1
Some details of hash manipulations:
HB_HCOPY() function copies a hash to another.
Syntax :
HB_HCOPY( <hsDestination>, <hsSource>, [<nStart>], [<nCount>] ) ->
<hsDestination>
As noticed in syntax, copy operation may be limited by [<nStart>], [<nCount>] arguments.
But a hash may NOT built by “COPY” method; because <hsDestination> argument isn’t optional.
hFruits := { "fruits" => { "apple", "cherry", "apricot" } }
hFruits2 := HB_HCOPY( hFruits ) // Argument error !
Though it’s possible in two steps:
hFruits2 := HB_HASH() // Built first an empty hash
hFruits2 := HB_HCOPY(hFruits2, hFruits ) // copy second onto first
As a result, for hash copy process two hashes should be exist:
hFruits := { "fruits" => { "apple", "cherry", "apricot" } }
hDays := { "days" => { "sunday", "monday" } }
hFruits := HB_HCOPY( hFruits, hDays )
or
hFruits := { "fruits" => { "apple", "cherry", "apricot" } }
hDays := { "days" => { "sunday", "monday" } }
hTarget := HB_HASH()
hTarget := HB_HCOPY( hTarget, hFruits )
hTarget := HB_HCOPY( hTarget, hDays )
HB_HMERGE() function merge two hashes.
Syntax:
HB_HMERGE( <hsDestination>, <hsSource>, <bBlock>|<nPosition> ) ->
<hsDestination>
hFruits := { "fruits" => { "apple", "cherry", "apricot" } }
hDays := { "days" => { "sunday", "monday" } }
hMerged := HB_HMERGE( hFruits, hDays )
hFruits :
1 days => sunday monday
2 fruits => apple cherry apricot
hTarget :
1 days => sunday monday
2 fruits => apple cherry apricot
AADD( hFruits[ "fruits" ], "melon" )
hFruits and hTarget :
1 days => sunday monday
2 fruits => apple cherry apricot melon
Result of above tests :
HB_HCOPY() and HB_HMERGE() doesn’t “physically” copy / merge hashes data; instead, copy / merge only by reference(s).
HB_HCLONE() function : Cloning (exact copy of) hashes.
Syntax:
HB_HCLONE( <hsTable> ) -> <hsDestination>
hFruits := { "fruits" => { "apple", "cherry", "apricot" } }
hClone := HB_HCLONE( hFruits )
hClone : fruits => apple cherry apricot
AADD( hFruits[ "fruits" ], "melon" ) // Source changed
hClone : fruits => apple cherry apricot
*-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._./*
Hash Details - 1
Copy, Merge & Clone Hashes.
*/
#define NTrim( x ) IF( HB_ISNUMERIC( x ), LTRIM( STR( x ) ), x )
PROCEDURE Main()
SET COLO TO "W/B"
cLMarj := SPACE( 3 )
CLS
? "Copy one hash to another : HB_HCOPY() function : "
? "Syntax :",;
"HB_HCOPY( <hsDestination>, <hsSource>, [<nStart>],"
? " [<nCount>] ) -> <hsDestination>"
hFruits := { "fruits" => { "apple", "cherry", "apricot" } }
hDays := { "days" => { "sunday", "monday" } }
* hFruits2 := HB_HCOPY( hFruits ) // Argument error !
hFruits := HB_HCOPY( hFruits, hDays )
ListHash( hFruits, "Copied-1 (Fruits)" )
hDays[ "days" ] := "friday"
ListHash( hFruits, "copied or referenced ?" )
hTarget := HB_HASH()
hFruits := { "fruits" => { "apple", "cherry", "apricot" } }
hDays := { "days" => { "sunday", "monday" } }
hTarget := HB_HCOPY( hTarget, hFruits )
hTarget := HB_HCOPY( hTarget, hDays )
ListHash( hTarget, "Copied-2 ( Target )" )
AADD( hFruits[ "fruits" ], "melon" )
ListHash( hTarget, "copied or referenced ?" )
? "Merge two hashes : HB_HMERGE() function : "
? "Syntax :",;
"HB_HMERGE( <hsDestination>, <hsSource>, <bBlock>|"
? " <nPosition> ) -> <hsDestination>"
hFruits := { "fruits" => { "apple", "cherry", "apricot" } }
hDays := { "days" => { "sunday", "monday" } }
hMerged := HB_HMERGE( hFruits, hDays )
ListHash( hFruits, "Merged (hFruits)" )
ListHash( hMerged, "Merged (hTarget)" )
AADD( hFruits[ "fruits" ], "melon" )
ListHash( hFruits, "Merged or referenced ? ( hFruits) " )
ListHash( hMerged, "Merged or referenced ? ( hMerged) " )
*
* Result of above tests :
*
* HB_HCOPY() and HB_HMERGE() doesn't "physically" copy / merge hashes data;
*
* instead copy / merge only by reference(s).
*
? "Cloning (exact copy of) hashes : HB_HCLONE() function : "
? "Syntax :",;
"HB_HCLONE( <hsTable> ) -> <hsDestination>"
hFruits := { "fruits" => { "apple", "cherry", "apricot" } }
hClone := HB_HCLONE( hFruits )
ListHash( hClone, "Cloned" )
AADD( hFruits[ "fruits" ], "melon" )
ListHash( hClone, "Source changed" )
?
@ MAXROW(), 0
WAIT "EOF HashDetails-1.prg"
RETURN // HashDetails-1.Main()
*-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.
PROCEDURE ListHash( hHash, cComment )
LOCAL x1Pair := NIL
cComment := IF( HB_ISNIL( cComment ), '', cComment )
? cComment, ''
* ?? "-- Type :", VALTYPE( hHash ),''
* ?? "size:", NTrim ( LEN( hHash ) )
?
FOR EACH x1Pair IN hHash
nIndex := x1Pair:__ENUMINDEX()
x1Key := x1Pair:__ENUMKEY()
x1Value := x1Pair:__ENUMVALUE()
? cLMarj, NTrim( nIndex )
* ?? '', VALTYPE( x1Pair )
?? '', NTrim( x1Key ), "=>"
* ?? '', VALTYPE( x1Key )
* ?? VALTYPE( x1Value )
IF HB_ISARRAY( x1Value )
AEVAL( x1Value, { | x1 | QQOUT( '', x1 ) } )
ELSE
?? '', NTrim( x1Value )
ENDIF
NEXT
? REPL( "~", 32 )
RETURN // ListHash()
*-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.

Hash Basics
Definition:
In general, a Hash Table, or Hash Array, or Associative array, or shortly Hash is an array- like data structure, to store some data with an associated key for each; so, ‘atom’ of a hash is a pair of a ‘key’ with a ‘value’. A hash system needs to perform at least three operations:
– add a new pair,
– access to value via key
– the search and delete operations on a key pair
In Harbour, a hash is simply a special array, or more precisely a “keyed” array with special syntax with a set of functions.
Building:
The “=>” operator can be used to indicate literally the relation between <key> <value> pair: <key> => <value>
We can define and initialize a hash by this “literal” way :
hDigits_1 := { 1 => 1, 2 => 2, 3 => 3, 4 => 4 }
or by a special function call:
hDigits_1 := HB_HASH( 1, 1, 2, 2, 3, 3, 4, 4 )
Using “add” method may be another way :
hDigits_1 := { => } // Build an empty hash
hDigits_1[ 1] := 1
hDigits_1[ 2] := 2
hDigits_1[ 3] := 3
hDigits_1[ 4] := 4
In this method while evaluating each of above assignments, if given key exits in hash, will be replaced its value; else add a new pair to the hash.
In addition, data can be added to a hash by extended “+=” operator:
hCountries := { 'Argentina' => "Buenos Aires" }
hCountries += { 'Brasil' => "Brasilia" }
hCountries += { 'Chile' => "Santiago" }
hCountries += { 'Mexico' => "Mexico City" }
Hashs may add ( concatenate ) each other by extended “+” sign :
hFruits := { "fruits" => { "apple", "chery", "apricot" } }
hDays := { "days" => { "sunday", "monday" } }
hDoris := hFruits + hDays
Note: This “+” and “+=” operators depends xHB lib and needs to xHB lib and xHB.ch.
Typing :
<key> part of a hash may be any legal scalar type : C, D, L, N; and <value> part may be in addition scalar types, any complex type ( array or hash ).
Correction : This definition is wrong ! The correct is :
<key> entry key; can be of type: number, date, datetime, string, pointer.
Corrected at : 2015.12.08; thanks to Marek.
hDigits_2 := { 1 => “One”, 2 => “Two”, 3 => “Three”, 4 => “Four” }
hDigits_3 := { "1" => "One", "2" => "Two", "3" => "Three", "4" => "Four" }
hDigits_4 := { "1" => "One", 2 => "Two", 3 => "Three", "4" => "Four" }
hDigits_5 := { 1 => "One", 1 => "Two", 3 => "Three", 4 => "Four"
All of these examples are legal. As a result, a pair record of a hash may be:
– Numeric key, numeric value ( hDigits_1 )
– Numeric key, character value ( hDigits_2 )
– Character key, character value ( hDigits_3 )
– Mixed type key ( hDigits_4 )
Duplicate keys (as seen in hDigits_5) is permitted to assign, but not give a result such as double keyed values: LEN( hDigits_5 ) is 3, not 4; because first pair replaced by second due to has same key.
Consider a table-like data for customers records with two character fields: Customer ID and customer name:
| Cust_ID | Cust_Name |
| CC001 | Pierce Firth |
| CC002 | Stellan Taylor |
| CC003 | Chris Cherry |
| CC004 | Amanda Baranski |
We can build a hash with this data :
hCustomers := { "CC001" => "Pierce Firth",;
"CC002" => "Stellan Taylor",;
"CC003" => "Chris Cherry",;
"CC004" => "Amanda Baranski" }
and list it:
?
? "Listing a hash :"
?
h1Record := NIL
FOR EACH h1Record IN hCustomers
? cLMarj, h1Record:__ENUMKEY(), h1Record:__ENUMVALUE()
NEXT
Accessing a specific record is easy :
hCustomers[ "CC003" ] // Chris Cherry
*-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.
/*
Hash Basics
*/
#include "xhb.ch"
#define NTrim( n ) LTRIM( STR( n ) )
PROCEDURE Main()
SET DATE GERM
SET CENT ON
SET COLO TO "W/B"
cLMarj := SPACE( 3 )
CLS
hDigits_1 := { => } // Build an empty hash
hDigits_1[ 1 ] := 1
hDigits_1[ 2 ] := 2
hDigits_1[ 3 ] := 3
hDigits_1[ 4 ] := 4
ListHash( hDigits_1, "Digits_1" )
hDigits_2 := HB_HASH( 1, 1, 2, 2, 3, 3, 4, 4 )
ListHash( hDigits_2, "Digits_2" )
hDigits_3 := { 1 => 1,;
2 => 2,;
3 => 3,;
4 => 4 }
ListHash( hDigits_3, "Digits_3" )
hDigits_4 := { 1 => "One",;
2 => "Two",;
3 => "Three",;
4 => "Four" }
ListHash( hDigits_4, "Digits_4" )
hDigits_5 := { "1" => "One",;
"2" => "Two",;
"3" => "Three",;
"4" => "Four" }
ListHash( hDigits_5, "Digits_5" )
hDigits_6 := { "1" => "One",;
2 => "Two",;
3 => "Three",;
"4" => "Four" }
ListHash( hDigits_6, "Digits_6" )
hDigits_7 := { 1 => "One",;
1 => "Two",; // This line replace to previous due to same key
3 => "Three",;
4 => "Four" }
ListHash( hDigits_7, "Digits_7" )
* WAIT "EOF digits"
hCustomers := { "CC001" => "Pierce Firth",;
"CC002" => "Stellan Taylor",;
"CC003" => "Chris Cherry",;
"CC004" => "Amanda Baranski" }
ListHash( hCustomers, "A hash defined and initialized literally" )
?
? "Hash value with a specific key (CC003) :", hCustomers[ "CC003" ] // Chris Cherry
?
cKey := "CC003"
?
? "Locating a specific record in an hash by key (", cKey, ":"
?
c1Data := hCustomers[ cKey ]
? cLMarj, c1Data
hCountries := { 'Argentina' => "Buenos Aires" }
hCountries += { 'Brasil' => "Brasilia" }
hCountries += { 'Chile' => "Santiago" }
hCountries += { 'Mexico' => "Mexico City" }
ListHash( hCountries, "A hash defined and initialized by adding with '+=' operator:" )
hFruits := { "fruits" => { "apple", "chery", "apricot" } }
hDays := { "days" => { "sunday", "monday" } }
hDoris := hFruits + hDays
ListHash( hDoris, "A hash defined and initialized by concataned two hash with '+' operator:" )
?
@ MAXROW(), 0
WAIT "EOF HashBasics.prg"
RETURN // HashBasics.Main()
*-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.
PROCEDURE ListHash( hHash, cComment )
LOCAL x1Pair := NIL
cComment := IF( HB_ISNIL( cComment ), '', cComment )
?
? cComment, "-- Type :", VALTYPE( hHash ), "size:", NTrim ( LEN( hHash ) )
?
FOR EACH x1Pair IN hHash
nIndex := x1Pair:__ENUMINDEX()
x1Key := x1Pair:__ENUMKEY()
x1Value := x1Pair:__ENUMVALUE()
? cLMarj, NTrim( nIndex )
* ?? '', VALTYPE( x1Pair )
?? '', x1Key, "=>"
* ?? '', VALTYPE( x1Key )
* ?? VALTYPE( x1Value )
IF HB_ISARRAY( x1Value )
AEVAL( x1Value, { | x1 | QQOUT( '', x1 ) } )
ELSE
?? '', x1Value
ENDIF
NEXT
RETURN // ListHash()
*-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.

Operator overloading
/*
Operator overloading
Some operators overloaded by extending their functionalities.
"$" was an operator for "checking substring existence in a string"
For example :
? "A" $ "ABC" // Result: .T.
? "Z" $ "ABC" // Result: .F.
Now, this operator can be used for arrays and hashs too, not only strings.
See examples below.
"=>" was a preprocessor operator with meaning "translate to : ...".
Now, this operator can be used as a <key> - <value> separator in Hashs
for define and / or assign <key> - <value> to Hashs.
See examples below.
"[ ]" was Array element indicator (Special)
"{ }" was Literal array and code block delimiters (Special)
Now, this indicators can be used for hashs too.
See examples below.
"+=" is self-increment operator that can be used both numeric
and string values.
Such as :
cTest := "This"
cTest += " is"
? cTest // This is
nTest := 3
nTest += 10
? nTest // 13
Now, this operator can be used for adding elements to an existing hash;
( but no for arrays ! ).
Note : Extended functionalities of $ and += operators depends xHB lib.
So need this usages to xHB lib and xHB.ch.
See examples below.
*/
#include "xhb.ch"
PROCEDURE Main()
CLS
aFruits := { "apple", "appricot", "cherry", "melon", "pear", "mulberry" }
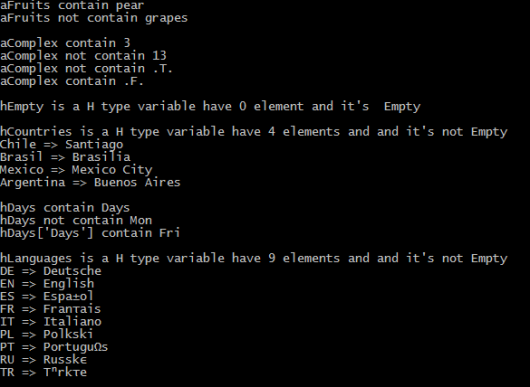
? "aFruits", IF( "pear" $ aFruits, '', 'not ' ) + "contain pear"
? "aFruits", IF( "grapes" $ aFruits, '', 'not ' ) +"contain grapes"
aComplex := ARRAY( 10 )
AEVAL( aComplex, { | x1, i1 | aComplex[ i1 ] := i1 } )
aComplex[ 5 ] := DATE()
aComplex[ 7 ] := .F.
?
? "aComplex", IF( 3 $ aComplex, '', 'not ' ) + "contain 3"
? "aComplex", IF( 13 $ aComplex, '', 'not ' ) + "contain 13"
? "aComplex", IF( .T. $ aComplex, '', 'not ' ) + "contain .T."
? "aComplex", IF( .F. $ aComplex, '', 'not ' ) + "contain .F."
hEmpty := { => }
?
? "hEmpty is a", VALTYPE( hEmpty ), "type variable have",;
STR( LEN( hEmpty ), 1 ), "element and it's",;
IF( EMPTY( hEmpty ), '', 'not' ), "Empty"
hCountries := { 'Argentina' => "Buenos Aires" }
hCountries += { 'Brasil' => "Brasilia" }
hCountries += { 'Chile' => "Santiago" }
hCountries += { 'Mexico' => "Mexico City" }
?
? "hCountries is a", VALTYPE( hCountries ), "type variable have",;
STR( LEN( hCountries ), 1 ), "elements and and it's",;
IF( EMPTY( hCountries ), '', 'not' ), "Empty"
cCountry := NIL
FOR EACH cCountry IN hCountries
? cCountry:__ENUMKEY(), "=>", cCountry:__ENUMVALUE()
NEXT
hDays := { 'Days' => { "Mon", "Tue", "Wed", "Thu", "Fri", "Sat", "Sun" } }
?
? "hDays", IF( 'Days' $ hDays, '', 'not ' ) + "contain Days"
? "hDays", IF( "Mon" $ hDays, '', 'not ' ) + "contain Mon"
? "hDays['Days']", IF( "Fri" $ hDays["Days"], '', 'not ' ) + "contain Fri"
hLanguages := { "EN" => "English" } +;
{ "DE" => "Deutsche" } +;
{ "ES" => "Español" } +;
{ "FR" => "Français" } +;
{ "IT" => "Italiano" } +;
{ "PL" => "Polkski" } +;
{ "PT" => "Português" } +;
{ "RU" => "Russkî" } +;
{ "TR" => "Türkçe" }
?
? "hLanguages is a", VALTYPE( hLanguages ), "type variable have",;
STR( LEN( hLanguages ), 1 ), "elements and and it's",;
IF( EMPTY( hLanguages ), '', 'not' ), "Empty"
cLanguage := NIL
FOR EACH cLanguage IN hLanguages
? cLanguage:__ENUMKEY(), "=>", cLanguage:__ENUMVALUE()
NEXT
@ MAXROW(), 0
WAIT "EOF OprOLoad.prg"
RETURN // OprOLoad.Prg.Main()
Code block basics
Strong Relation
C5 Data Manipulation Functions
Array :
AADD() :
Add a new element to the end of an array
AADD( <aTarget>, <expValue> ) --> Value
ACLONE() :
Duplicate a nested or multidimensional array
ACLONE( <aSource> ) --> aDuplicate
ACOPY() :
Copy elements from one array to another
ACOPY( <aSource>, <aTarget>, [ <nStart> ], [ <nCount> ],
[ <nTargetPos> ] ) --> aTarget
ADEL() :
Delete an array element
ADEL( <aTarget>, <nPosition> ) --> aTarget
ADIR()* :
Fill a series of arrays with directory information
ADIR([ <cFilespec> ],
[ <aFilenames> ],
[ <aSizes> ],
[ <aDates> ],
[ <aTimes> ],
[ <aAttributes> ] ) --> nFiles
AEVAL() :
Execute a code block for each element in an array
AEVAL( <aArray>, <bBlock>, [ <nStart> ], [ <nCount> ] ) --> aArray
AFILL() :
Fill an array with a specified value
AFILL( <aTarget>, <expValue>, [ <nStart> ], [ <nCount> ] )
--> aTarget
AINS() :
Insert a NIL element into an array
AINS( <aTarget>, <nPosition> ) --> aTarget
ARRAY() :
Create an uninitialized array of specified length
ARRAY( <nElements> [, <nElements>...] ) --> aArray
ASCAN() :
Scan an array for a value or until a block returns (.T.)
ASCAN( <aTarget>, <expSearch>, [ <nStart> ], [ <nCount> ] )
--> nStoppedAt
ASIZE() :
Grow or shrink an array
ASIZE( <aTarget>, <nLength> ) --> aTarget
ASORT() :
Sort an array
ASORT( <aTarget>, [ <nStart> ], [ <nCount> ], [ <bOrder> ] )
--> aTarget
ATAIL() :
Return value of the highest numbered (last) element of an array
ATAIL( <aArray> ) --> Element
Common :
EMPTY() :
Determine if the result of an expression is empty
EMPTY( <exp> ) --> lEmpty
LEN() :
Return the length of a character string or array size
LEN( <cString> | <aArray> ) --> nCount
MAX() :
Return the larger of two numeric or date values
MAX( <nExp1>, <nExp2> ) --> nLarger MAX( <dExp1>, <dExp2> ) --> dLarger
MIN() :
Return the smaller of two numeric or date values
MIN( <nExp1>, <nExp2> ) --> nSmaller MIN( <dExp1>, <dExp2> ) --> dSmaller
PAD() :
Pad character, date or numeric values with a fill character
PADL( <exp>, <nLength>, [ <cFillChar> ] ) --> cPaddedString PADC( <exp>, <nLength>, [ <cFillChar> ] ) --> cPaddedString PADR( <exp>, <nLength>, [ <cFillChar> ] ) --> cPaddedString
TRANSFORM() :
Convert any value into a formatted character string
TRANSFORM( <exp>, <cSayPicture> ) --> cFormatString
TYPE() :
Determine the type of an expression
TYPE( <cExp> ) --> cType
VALTYPE() :
Determine the data type returned by an expression
VALTYPE( <exp> ) --> cType
Date & Time :
CDOW() :
Convert a date value to a character day of the week
CDOW( <dExp> ) --> cDayName
CMONTH() :
Convert a date to a character month name
CMONTH( <dDate> ) --> cMonth
CTOD() :
Convert a date string to a date value
CTOD( <cDate> ) --> dDate
DATE() :
Return the system date as a date value
DATE() --> dSystem
DAY() :
Return the day of the month as a numeric value
DAY( <dDate> ) --> nDay
DOW() :
Convert a date value to a numeric day of the week
DOW( <dDate> ) --> nDay
DTOC() :
Convert a date value to a character string
DTOC( <dDate> ) --> cDate
DTOS() :
Convert a date value to a string formatted as yyyymmdd
DTOS( <dDate> ) --> cDate
MONTH() :
Convert a date value to the number of the month
MONTH( <dDate> ) --> nMonth
SECONDS() :
Return the number of seconds elapsed since midnight
SECONDS() --> nSeconds
TIME() :
Return the system time
TIME() --> cTimeString
YEAR() :
Convert a date value to the year as a numeric value
YEAR( <dDate> ) --> nYear
Numeric :
ABS() :
Return the absolute value of a numeric expression
ABS( <nExp> ) --> nPositive
BIN2I() :
Convert a 16-bit signed integer to a numeric value
BIN2I( <cSignedInt> ) --> nNumber
BIN2L() :
Convert a 32-bit signed integer to a numeric value
BIN2L( <cSignedInt> ) --> nNumber
BIN2W() :
Convert a 16-bit unsigned integer to a numeric value
BIN2W( <cUnsignedInt> ) --> nNumber
EXP() :
Calculate e**x
EXP( <nExponent> ) --> nAntilogarithm
INT() :
Convert a numeric value to an integer
INT( <nExp> ) --> nInteger
I2BIN() :
Convert a numeric to a 16-bit binary integer
I2BIN( <nInteger> ) --> cBinaryInteger
LOG() :
Calculate the natural logarithm of a numeric value
LOG( <nExp> ) --> nNaturalLog
L2BIN() :
Convert a numeric value to a 32-bit binary integer
L2BIN( <nExp> ) --> cBinaryInteger
MOD()* :
Return dBASE III PLUS modulus of two numbers
MOD( <nDividend>, <nDivisor> ) --> nRemainder
ROUND() :
Return a value rounded to a specified number of digits
ROUND( <nNumber>, <nDecimals> ) --> nRounded
SQRT() :
Return the square root of a positive number
SQRT( <nNumber> ) --> nRoot
VAL() :
Convert a character number to numeric type
VAL( <cNumber> ) --> nNumber
String & Memo :
ALLTRIM() :
Remove leading and trailing spaces from character string
ALLTRIM( <cString> ) --> cTrimString
ASC() :
Convert a character to its ASCII value
ASC( <cExp> ) --> nCode
AT() :
Return the position of a substring within a string
AT( <cSearch>, <cTarget> ) --> nPosition
CHR() :
Convert an ASCII code to a character value
CHR( <nCode> ) --> cChar
HARDCR() :
Replace all soft CRs with hard CRs
HARDCR( <cString> ) --> cConvertedString
ISALPHA() :
Determine if the leftmost character is alphabetic
ISALPHA( <cString> ) --> lBoolean
ISDIGIT() :
Determine if the leftmost character is a digit
ISDIGIT( <cString> ) --> lBoolean
ISLOWER() :
Determine if the leftmost character is a lower case letter
ISLOWER( <cString> ) --> lBoolean
ISUPPER() :
Determine if the leftmost character is upper case
ISUPPER( <cString> ) --> lBoolean
LEFT() :
Extract a substring beginning with the first character
LEFT( <cString>, <nCount> ) --> cSubString
LOWER() :
Convert uppercase characters to lowercase
LOWER( <cString> ) --> cLowerString
LTRIM() :
Remove leading spaces from a character string
LTRIM( <cString> ) --> cTrimString
MEMOEDIT() :
Display or edit character strings and memo fields
MEMOEDIT( [ <cString> ],
[ <nTop> ], [ <nLeft> ],
[ <nBottom> ], [ <nRight> ],
[ <lEditMode> ],
[ <cUserFunction> ],
[ <nLineLength> ],
[ <nTabSize> ],
[ <nTextBufferRow> ],
[ <nTextBufferColumn> ],
[ <nWindowRow> ],
[ <nWindowColumn> ] ) --> cTextBuffer
MEMOLINE() :
Extract a line of text from character string or memo field
MEMOLINE( <cString>,
[ <nLineLength> ],
[ <nLineNumber> ],
[ <nTabSize> ],
[ <lWrap> ] ) --> cLine
MEMOREAD() :
Return the contents of a disk file as a character string
MEMOREAD( <cFile> ) --> cString
MEMOTRAN() :
Replace carriage return/line feeds in character strings
MEMOTRAN( <cString>,
[ <cReplaceHardCR> ],
[ <cReplaceSoftCR> ] ) --> cNewString
MEMOWRIT() :
Write a character string or memo field to a disk file
MEMOWRIT( <cFile>, <cString> ) --> lSuccess
MLCOUNT() :
Count the lines in a character string or memo field
MLCOUNT( <cString>, [ <nLineLength> ], [ <nTabSize> ],
[ <lWrap> ] ) --> nLines
MLCTOPOS() :
Return byte position based on line and column position
MLCTOPOS( <cText>, <nWidth>, <nLine>,
<nCol>, [ <nTabSize> ], [ <lWrap> ] ) --> nPosition
MLPOS() :
Determine the position of a line in a memo field
MLPOS( <cString>, <nLineLength>,
<nLine>, [ <nTabSize> ], [ <lWrap> ] ) --> nPosition
MPOSTOLC() :
Return line and column position based on byte position
MPOSTOLC( <cText>, <nWidth>, <nPos>,
[ <nTabSize> ], [ <lWrap> ] ) --> aLineColumn
RAT() :
Return the position of the last occurrence of a substring
RAT( <cSearch>, <cTarget> ) --> nPosition
REPLICATE() :
Return a string repeated a specified number of times
REPLICATE( <cString>, <nCount> ) --> cRepeatedString
RIGHT() :
Return a substring beginning with rightmost character
RIGHT( <cString>, <nCount> ) --> cSubString
RTRIM() :
Remove trailing spaces from a character string
RTRIM( <cString> ) --> cTrimString
SET EXACT* :
Toggle exact matches for character strings
SET EXACT on | OFF | <xlToggle>
SOUNDEX() :
Convert a character string to soundex form
SOUNDEX( <cString> ) --> cSoundexString
SPACE() :
Return a string of spaces
SPACE( <nCount> ) --> cSpaces
STR() :
Convert a numeric expression to a character string
STR( <nNumber>, [ <nLength> ], [ <nDecimals> ] ) --> cNumber
STRTRAN() :
Search and replace characters within a character string
STRTRAN( <cString>, <cSearch>, [ <cReplace> ],
[ <nStart> ], [ <nCount> ] ) --> cNewString
STUFF() :
Delete and insert characters in a string
STUFF( <cString>, <nStart>, <nDelete>, <cInsert> ) --> cNewString
SUBSTR() :
Extract a substring from a character string
SUBSTR( <cString>, <nStart>, [ <nCount> ] ) --> cSubstring
TRIM() :
Remove trailing spaces from a character string
TRIM( <cString> ) --> cTrimString
UPPER() :
Convert lowercase characters to uppercase
UPPER( <cString> ) --> cUpperString
Where Is It ?
Produces a message that say program execution point and backward calling sequence; for debugging purposes.
Download here ( source only ).
