Tag Archives: MAX()
Harbour Math Functions
Min()
MIN()
Determines the minumum of two numbers or dates.
Syntax
MIN( <xValue>, <xValue1> ) --> <xMin>
Arguments
<xValue> Any date or numeric value.
<xValue1> Any date or numeric value.
Returns
<xMin> The smaller numeric (or earlier date) value.
Description
This function returns the smaller of the two passed espressions. <xValue> and <xValue1> must be the same data type. If numeric, the smaller number is returned. If dates, the earlier date is returned.
Examples
? MIN( 214514214, 6251242142 )
? MIN( STOD( "20001111" ), STOD( "20140621" ) )
Compliance
Clipper
Platforms
All
Files
Library is rtl
Seealso
MAX()
Max()
MAX()
Returns the maximum of two numbers or dates.
Syntax
MAX( <xValue>, <xValue1> ) --> <xMax>
Arguments
<xValue> Any date or numeric value.
<xValue1> Any date or numeric value (same type as <xValue>).
Returns
<xMax> The larger numeric (or later date) value.
Description
This function returns the larger of the two passed espressions. If <xValue> and <xValue1> are numeric data types, the value returned by this function will be a numeric data type as well and will be the larger of the two numbers passed to it. If <xValue> and <xValue1> are date data types, the return value will be a date data type as well. It will be the later of the two dates passed to it.
Examples
? MAX( 214514214, 6251242142 )
? MAX( STOD( "20001111" ), STOD( "20140621" ) )
Compliance
Clipper
Platforms
All
Files
Library is rtl
Seealso
Min()
C5_MAX
MAX()
Return the larger of two numeric or date values
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Syntax
MAX(<nExp1>, <nExp2>) --> nLarger
MAX(<dExp1>, <dExp2>) --> dLarger
Arguments
<nExp1> and <nExp2> are the numeric values to be compared.
<dExp1> and <dExp2> are the date values to be compared.
Returns
MAX() returns the larger of the two arguments. The value returned is
the same type as the arguments.
Description
MAX() is a numeric and date function that ensures the value of an
expression is larger than a specified minimum. The inverse of MAX() is
MIN(), which returns the lesser of two numeric or date values.
Examples
. In these examples MAX() returns the greater of two numeric
values:
? MAX(1, 2) // Result: 2
? MAX(2, 1) // Result: 2
. In these examples MAX() compares date values:
? DATE() // Result: 09/01/90
? MAX(DATE(), DATE() + 30) // Result: 10/01/90
? MAX(DATE(), CTOD("")) // Result: 09/01/90
Files Library is CLIPPER.LIB.
See Also: MIN()
Code blocks, inside and out
Code blocks, inside and out
C5 Data Manipulation Functions
Array :
AADD() :
Add a new element to the end of an array
AADD( <aTarget>, <expValue> ) --> Value
ACLONE() :
Duplicate a nested or multidimensional array
ACLONE( <aSource> ) --> aDuplicate
ACOPY() :
Copy elements from one array to another
ACOPY( <aSource>, <aTarget>, [ <nStart> ], [ <nCount> ],
[ <nTargetPos> ] ) --> aTarget
ADEL() :
Delete an array element
ADEL( <aTarget>, <nPosition> ) --> aTarget
ADIR()* :
Fill a series of arrays with directory information
ADIR([ <cFilespec> ],
[ <aFilenames> ],
[ <aSizes> ],
[ <aDates> ],
[ <aTimes> ],
[ <aAttributes> ] ) --> nFiles
AEVAL() :
Execute a code block for each element in an array
AEVAL( <aArray>, <bBlock>, [ <nStart> ], [ <nCount> ] ) --> aArray
AFILL() :
Fill an array with a specified value
AFILL( <aTarget>, <expValue>, [ <nStart> ], [ <nCount> ] )
--> aTarget
AINS() :
Insert a NIL element into an array
AINS( <aTarget>, <nPosition> ) --> aTarget
ARRAY() :
Create an uninitialized array of specified length
ARRAY( <nElements> [, <nElements>...] ) --> aArray
ASCAN() :
Scan an array for a value or until a block returns (.T.)
ASCAN( <aTarget>, <expSearch>, [ <nStart> ], [ <nCount> ] )
--> nStoppedAt
ASIZE() :
Grow or shrink an array
ASIZE( <aTarget>, <nLength> ) --> aTarget
ASORT() :
Sort an array
ASORT( <aTarget>, [ <nStart> ], [ <nCount> ], [ <bOrder> ] )
--> aTarget
ATAIL() :
Return value of the highest numbered (last) element of an array
ATAIL( <aArray> ) --> Element
Common :
EMPTY() :
Determine if the result of an expression is empty
EMPTY( <exp> ) --> lEmpty
LEN() :
Return the length of a character string or array size
LEN( <cString> | <aArray> ) --> nCount
MAX() :
Return the larger of two numeric or date values
MAX( <nExp1>, <nExp2> ) --> nLarger MAX( <dExp1>, <dExp2> ) --> dLarger
MIN() :
Return the smaller of two numeric or date values
MIN( <nExp1>, <nExp2> ) --> nSmaller MIN( <dExp1>, <dExp2> ) --> dSmaller
PAD() :
Pad character, date or numeric values with a fill character
PADL( <exp>, <nLength>, [ <cFillChar> ] ) --> cPaddedString PADC( <exp>, <nLength>, [ <cFillChar> ] ) --> cPaddedString PADR( <exp>, <nLength>, [ <cFillChar> ] ) --> cPaddedString
TRANSFORM() :
Convert any value into a formatted character string
TRANSFORM( <exp>, <cSayPicture> ) --> cFormatString
TYPE() :
Determine the type of an expression
TYPE( <cExp> ) --> cType
VALTYPE() :
Determine the data type returned by an expression
VALTYPE( <exp> ) --> cType
Date & Time :
CDOW() :
Convert a date value to a character day of the week
CDOW( <dExp> ) --> cDayName
CMONTH() :
Convert a date to a character month name
CMONTH( <dDate> ) --> cMonth
CTOD() :
Convert a date string to a date value
CTOD( <cDate> ) --> dDate
DATE() :
Return the system date as a date value
DATE() --> dSystem
DAY() :
Return the day of the month as a numeric value
DAY( <dDate> ) --> nDay
DOW() :
Convert a date value to a numeric day of the week
DOW( <dDate> ) --> nDay
DTOC() :
Convert a date value to a character string
DTOC( <dDate> ) --> cDate
DTOS() :
Convert a date value to a string formatted as yyyymmdd
DTOS( <dDate> ) --> cDate
MONTH() :
Convert a date value to the number of the month
MONTH( <dDate> ) --> nMonth
SECONDS() :
Return the number of seconds elapsed since midnight
SECONDS() --> nSeconds
TIME() :
Return the system time
TIME() --> cTimeString
YEAR() :
Convert a date value to the year as a numeric value
YEAR( <dDate> ) --> nYear
Numeric :
ABS() :
Return the absolute value of a numeric expression
ABS( <nExp> ) --> nPositive
BIN2I() :
Convert a 16-bit signed integer to a numeric value
BIN2I( <cSignedInt> ) --> nNumber
BIN2L() :
Convert a 32-bit signed integer to a numeric value
BIN2L( <cSignedInt> ) --> nNumber
BIN2W() :
Convert a 16-bit unsigned integer to a numeric value
BIN2W( <cUnsignedInt> ) --> nNumber
EXP() :
Calculate e**x
EXP( <nExponent> ) --> nAntilogarithm
INT() :
Convert a numeric value to an integer
INT( <nExp> ) --> nInteger
I2BIN() :
Convert a numeric to a 16-bit binary integer
I2BIN( <nInteger> ) --> cBinaryInteger
LOG() :
Calculate the natural logarithm of a numeric value
LOG( <nExp> ) --> nNaturalLog
L2BIN() :
Convert a numeric value to a 32-bit binary integer
L2BIN( <nExp> ) --> cBinaryInteger
MOD()* :
Return dBASE III PLUS modulus of two numbers
MOD( <nDividend>, <nDivisor> ) --> nRemainder
ROUND() :
Return a value rounded to a specified number of digits
ROUND( <nNumber>, <nDecimals> ) --> nRounded
SQRT() :
Return the square root of a positive number
SQRT( <nNumber> ) --> nRoot
VAL() :
Convert a character number to numeric type
VAL( <cNumber> ) --> nNumber
String & Memo :
ALLTRIM() :
Remove leading and trailing spaces from character string
ALLTRIM( <cString> ) --> cTrimString
ASC() :
Convert a character to its ASCII value
ASC( <cExp> ) --> nCode
AT() :
Return the position of a substring within a string
AT( <cSearch>, <cTarget> ) --> nPosition
CHR() :
Convert an ASCII code to a character value
CHR( <nCode> ) --> cChar
HARDCR() :
Replace all soft CRs with hard CRs
HARDCR( <cString> ) --> cConvertedString
ISALPHA() :
Determine if the leftmost character is alphabetic
ISALPHA( <cString> ) --> lBoolean
ISDIGIT() :
Determine if the leftmost character is a digit
ISDIGIT( <cString> ) --> lBoolean
ISLOWER() :
Determine if the leftmost character is a lower case letter
ISLOWER( <cString> ) --> lBoolean
ISUPPER() :
Determine if the leftmost character is upper case
ISUPPER( <cString> ) --> lBoolean
LEFT() :
Extract a substring beginning with the first character
LEFT( <cString>, <nCount> ) --> cSubString
LOWER() :
Convert uppercase characters to lowercase
LOWER( <cString> ) --> cLowerString
LTRIM() :
Remove leading spaces from a character string
LTRIM( <cString> ) --> cTrimString
MEMOEDIT() :
Display or edit character strings and memo fields
MEMOEDIT( [ <cString> ],
[ <nTop> ], [ <nLeft> ],
[ <nBottom> ], [ <nRight> ],
[ <lEditMode> ],
[ <cUserFunction> ],
[ <nLineLength> ],
[ <nTabSize> ],
[ <nTextBufferRow> ],
[ <nTextBufferColumn> ],
[ <nWindowRow> ],
[ <nWindowColumn> ] ) --> cTextBuffer
MEMOLINE() :
Extract a line of text from character string or memo field
MEMOLINE( <cString>,
[ <nLineLength> ],
[ <nLineNumber> ],
[ <nTabSize> ],
[ <lWrap> ] ) --> cLine
MEMOREAD() :
Return the contents of a disk file as a character string
MEMOREAD( <cFile> ) --> cString
MEMOTRAN() :
Replace carriage return/line feeds in character strings
MEMOTRAN( <cString>,
[ <cReplaceHardCR> ],
[ <cReplaceSoftCR> ] ) --> cNewString
MEMOWRIT() :
Write a character string or memo field to a disk file
MEMOWRIT( <cFile>, <cString> ) --> lSuccess
MLCOUNT() :
Count the lines in a character string or memo field
MLCOUNT( <cString>, [ <nLineLength> ], [ <nTabSize> ],
[ <lWrap> ] ) --> nLines
MLCTOPOS() :
Return byte position based on line and column position
MLCTOPOS( <cText>, <nWidth>, <nLine>,
<nCol>, [ <nTabSize> ], [ <lWrap> ] ) --> nPosition
MLPOS() :
Determine the position of a line in a memo field
MLPOS( <cString>, <nLineLength>,
<nLine>, [ <nTabSize> ], [ <lWrap> ] ) --> nPosition
MPOSTOLC() :
Return line and column position based on byte position
MPOSTOLC( <cText>, <nWidth>, <nPos>,
[ <nTabSize> ], [ <lWrap> ] ) --> aLineColumn
RAT() :
Return the position of the last occurrence of a substring
RAT( <cSearch>, <cTarget> ) --> nPosition
REPLICATE() :
Return a string repeated a specified number of times
REPLICATE( <cString>, <nCount> ) --> cRepeatedString
RIGHT() :
Return a substring beginning with rightmost character
RIGHT( <cString>, <nCount> ) --> cSubString
RTRIM() :
Remove trailing spaces from a character string
RTRIM( <cString> ) --> cTrimString
SET EXACT* :
Toggle exact matches for character strings
SET EXACT on | OFF | <xlToggle>
SOUNDEX() :
Convert a character string to soundex form
SOUNDEX( <cString> ) --> cSoundexString
SPACE() :
Return a string of spaces
SPACE( <nCount> ) --> cSpaces
STR() :
Convert a numeric expression to a character string
STR( <nNumber>, [ <nLength> ], [ <nDecimals> ] ) --> cNumber
STRTRAN() :
Search and replace characters within a character string
STRTRAN( <cString>, <cSearch>, [ <cReplace> ],
[ <nStart> ], [ <nCount> ] ) --> cNewString
STUFF() :
Delete and insert characters in a string
STUFF( <cString>, <nStart>, <nDelete>, <cInsert> ) --> cNewString
SUBSTR() :
Extract a substring from a character string
SUBSTR( <cString>, <nStart>, [ <nCount> ] ) --> cSubstring
TRIM() :
Remove trailing spaces from a character string
TRIM( <cString> ) --> cTrimString
UPPER() :
Convert lowercase characters to uppercase
UPPER( <cString> ) --> cUpperString
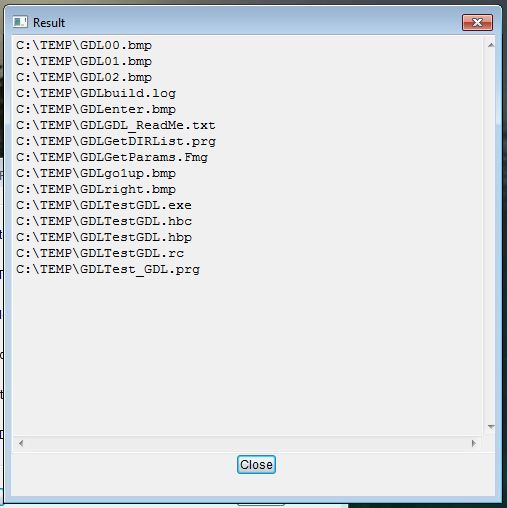
Directory List
Reinvention of wheel ?
Not quite …
Main difference is allowing file(s) and folder(s) selection together.
Another difference is implementing of <lNoChangeDir> parameter. Unlike GetFile(), GetDIRList() uses this value for allowing change directory ability to user.
Furthermore sorting grid columns by three (not two) ways, GetVolumLabel(), List2Arry() and Arry2List() functions may be useful.
Also, test program ( TestGDL.prg ) may be a sample for .fmg based application.
Download here ( source only ).
Hex View
Hexadecimal file viewer.
This is a experimental project with first intend of point out the power of Harbour and HMG. So, HexView is considerably slow on large files, please be patient.
Download here ( source only ).