FIELDLENX() Returns length of field EXPBLOCK() Returns a codeblock to evaluate an expresson FIELDTYPEX() Returns type of field FIELDPOSX() Returns position of field named in expression FIELDDECX() Returns decimals of field PARSFIELD() Exracts the name of the field from an expression BLANKREC() Blanks out a record PARSALIAS() Exracts the name of the alias from an expression WORKBLOCK() Returns a set-get block for field named in an expression BLANKFIELD() Returns a blank value corresponding to a field ISBLANKREC() Determines if a record is blank ISFIELD() Determines if an expression is the name of a field ISTHISAREA() Determines if expression is the name of a field in this area
Tag Archives: expression
SP_WORKBLOCK
WORKBLOCK() Short: ------ WORKBLOCK() Returns a set-get block for field named in an expression Returns: -------- <bBlock> => a set-get block Syntax: ------- WORKBLOCK(cExpress) Description: ------------ Determines the work area and field name in <cExpress> and returns a FIELDWBLOCK() created block for it. Examples: --------- cExpr := "CUSTOMER->LNAME" bExpr := WORKBLOCK(cExpr) ?eval(bExpr) // displays value ?eval(bExpr,"SMITH") // sets new value Source: ------- S_FIELDS.PRG
SP_PARSFIELD
PARSFIELD()
Short:
------
PARSFIELD() Extracts the name of the field from an expression
Returns:
--------
<cField> => name of the field
Syntax:
-------
PARSFIELD(cExpress)
Description:
------------
Returns the field name part of cExpress
Examples:
---------
cExpr := "CUSTOMER->LASTNAME"
IF ISFIELD(cExpr)
?PARSALIAS(cExpr) // displays CUSTOMER
?PARSFIELD(cExpr) // displays LASTNAME
ENDIF
Warnings:
----------
Does not verify if this is a valid field. Use
ISFIELD().
Source:
-------
S_FIELDS.PRG
SP_PARSALIAS
PARSALIAS()
Short:
------
PARSALIAS() Extracts the name of the alias from an expression
Returns:
--------
<cAlias> => name of the alias
Syntax:
-------
PARSALIAS(cExpress)
Description:
------------
Returns the ALIAS part of cExpress. If <cExpress> is
not prefaced
with an alias ( XXXX-> ) the current ALIAS() is
returned.
Examples:
---------
cExpr := "CUSTOMER->LASTNAME"
IF ISFIELD(cExpr)
?PARSALIAS(cExpr) // displays CUSTOMER
?PARSFIELD(cExpr) // displays LASTNAME
ENDIF
Warnings:
----------
Does not verify if this is a valid field. Use
ISFIELD().
Source:
-------
S_FIELDS.PRG
SP_ISTHISAREA
ISTHISAREA()
Short:
------
ISTHISAREA() Determines if expression is the name of a field
in this area
Returns:
--------
<lIsThisArea> => Is the expression a field in this
area
Syntax:
-------
ISTHISAREA(cExpress)
Description:
------------
Determines if <cExpress> contains the name of a field
in this area.
If <cExpress> contains an alias, the area of the
alias will be checked.
ISTHISAREA() first calls ISFIELD() to ensure the
expression is a field name.
If a field in another area is passed, and no alias is
used, False will be returned.
Examples:
---------
ISTHISAREA("LASTNAME") // actual field, returns .t.
ISTHISAREA("CUSTOMER->LASTNAME") // actual field, returns .t.
ISTHISAREA("LEFT(LNAME,5)") // expression, returns .f.
ISTHISAREA("AGENT") //field, but in another area. Returns .f.
Notes:
-------
Companion functions are ISFIELD(), ISEDITABLE(),
PARSFIELD(), PARSALIAS(), EXPBLOCK(), WORKBLOCK()
Source:
-------
S_FIELDS.PRG
SP_ISNOTDUP
ISNOTDUP()
Short:
------
ISNOTDUP() Checks for a duplicate field
Returns:
--------
<lDup> => is duplicate field
Syntax:
-------
ISNOTDUP(expCurrent,[nOrder],[bCompare],;
[lBlankOk],[nExceptRec],[cMsg])
Description:
------------
Looks in the current DBF for <expCurrent> - an
expression of any type. [nOrder] is the index order to SEEK on.
Default is INDEXORD(). [bCompare] - in lieu of an index key,
this block is used in a locate compare of <expCurrent> as in
LOCATE FOR eval(bCompare)==expCurrent.
[lBlankOk] if <expCurrent> is blank, and this is
.f. (the default), then and automatic .f. is returned.
[nExceptRec] if this is passed, will check all BUT
this record number. Useful for editing routine, where you don't
wish to check for a duplicate of the existing record.
[cMsg] the message displayed if a duplicate is
found. Default is none.
Examples:
---------
@6,0 GET V6 valid ;
ISNOTDUP(v6,nil,nil,nil,nil,"Duplicate found")
@6,0 GET V6 valid ;
ISNOTDUP(v6,3,nil,nil,recno(),"Duplicate found")
@6,0 GET V6 valid ;
ISNOTDUP(v6,nil,{||afile->v6},nil,recno(),"Duplicate found")
Notes:
-------
Normally for use in making sure a duplicate record is
not entered.
Source:
-------
S_NOTDUP.PRG
SP_ISFIELD
ISFIELD() Short: ------ ISFIELD() Determines if an expression is the name of a field Returns: -------- <lIsfield> => Is the expression a field Syntax: ------- ISFIELD(cExpress) Description: ------------ Determines if <cExpress> contains the name of a field. If <cExpress> contains an alias, the area of the alias will be checked. Examples: --------- isfield( "LASTNAME" ) // actual field, returns .t. isfield( "CUSTOMER->LASTNAME") // actual field, returns .t. isfield( "LEFT(LNAME,5)" ) // expression, returns .f. Notes: ------- Companion functions are ISTHISAREA(), ISEDITABLE(), PARSFIELD(), PARSALIAS(), EXPBLOCK(), WORKBLOCK() Source: ------- S_FIELDS.PRG
SP_FORMULATE
FORMULATE()
Short:
------
FORMULATE() Builds a free-form formula or User Defined Field
Returns:
--------
<cFormula> => String containing formula
Syntax:
-------
FORMULATE([cInFormula],[aFields], [aFDesc], [cDisplay],[cTypes] )
Description:
------------
Allows ad hoc creation of formulas (expressions) by mixing freeform
text, function templates and operators.
[cInFormula] Optional character string containing the formula to
modify
[aFields] Optional list of dbf field names
[aFDesc ] Optional list of alternate names for dbf field names
[cDisplay] Optional text for the prompt. Default is :
"Create Formula/User Defined field:"
[cTypes] Optional string containing allowed return types (in caps)
Default is "CDNL" (char, date, numeric, logical)
Examples:
---------
1. cExpress := FORMULATE("",nil,nil,"Create logical expression","L")
2.(taken from FORMLETR() )
cAddExpress := FORMULATE(aEdit[nThisLine],aFieldNames,aFieldDesc,;
"Modify Label Contents (must result in type CHARACTER):",;
"C")
Notes:
-------
Source:
-------
S_FORMU.PRG
Harbour New Data types
Data type & Syntax extensions in Harbour
In addition to Clipper’s scalar ( Character, Number, Date, Logical, MEMO, Nil ) and complex ( array, CodeBlock ) data types; Harbour has extended data types: pointer as scalar and object and hach as complex type.
For standard data types please refer here and/or here.
In database files (tables) data types of fields are predefined in structure of table.
For extended field types please refer here.
For data items other than fields (such as variables and manifest constants); in general, type of data determined automatically by system, when assigning a value. The first basic way of this, is assigning a “literal” value.
For a working sample about constants please refer here.
cString := "This is a string" // A character string enclosed by a string delimiter
nNumber := 123.45 // A numeric value combined digits, decimal point and a sign ( + / - )
lTrue := .T. // A T (tYy) or F (fNn) letter enclosed by two periods (.)
aArray := {} // Arrays can be assigned literally by enclosed with curly brace
In addition to this basic literal value notations, Harbour has also extended notations:
– Data Types determined by special prefixs
— 0x… : Hexadecimal constant
nNumber := 0x0A // 0x prefix implies the string as Hexadecimal String
// and type of resulting value become as Numeric (N)
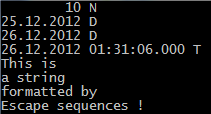
? nNumber, VALTYPE( nNumber ) // 10 N
— 0d… date constant
dDate_1 := 0d20121225 // 0d prefix implies the string a date string
// ( instead of using CTOD() )
// and type of resulting value become as Date (D)
? dDate_1, VALTYPE( dDate_1 ) // 25.12.2012 D
– Special literal string formats
— d”…” : Date constant
dDate_2 := d"2012-12-26" ? dDate_2, VALTYPE( dDate_2 ) // 26.12.2012 D
— t”…” : Time constant
tTime_1 := dDate_2 + t”01:31:06″
? tTime_1, VALTYPE( tTime_1 ) // 26.12.2012 01:31:06.000 T
— e”…” : Escape sequences
Escape sequences are used to define certain special characters within string literals.
( Prefix by “\” escape sequence codes within that string )
The following escape sequences are available in C and C++ language :
Escape
sequence Description Representation
' single quote byte 0x27
" double quote byte 0x22
? question mark byte 0x3f
backslash byte 0x5c
null character byte 0x00
a audible bell byte 0x07
b backspace byte 0x08
f form feed - new page byte 0x0c
n line feed - new line byte 0x0a
r carriage return byte 0x0d
t horizontal tab byte 0x09
v vertical tab byte 0x0b
nnn arbitrary octal value byte nnn
xnn arbitrary hexadecimal value byte nn
unnnn arbitrary Unicode value.
May result in several characters. code point U+nnnn
Unnnnnnnn arbitrary Unicode value.
May result in several characters. code point U+nnnnnnnn
Note that all sequences not available in Harbour.
For the new complex data type Hash, there is a literally assigning way :
hHash := { => } // => sign indicates the hash
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
PROCEDURE Main()
SET CENT ON
SET DATE GERM
CLS
* Data Types determined by special prefixs
** 0x... : Hexadecimal constant
nNumber := 0x0A // 0x prefix implies the string as Hexadecimal String
// and type of resulting value become as Numeric(D)
? nNumber, VALTYPE( nNumber ) // 10 N
** 0d... date constant
dDate_1 := 0d20121225 // 0d prefix implies the string a date string
// ( instead of using CTOD() )
// and type of resulting value become as Date (D)
? dDate_1, VALTYPE( dDate_1 ) // 25.12.2012 D
* Special literal string formats
** d"..." : Date constant
dDate_2 := d"2012-12-26"
? dDate_2, VALTYPE( dDate_2 ) // 26.12.2012 D
** t"..." : Time constant
tTime_1 := dDate_2 + t"01:31:06"
? tTime_1, VALTYPE( tTime_1 ) // 26.12.2012 01:31:06.000 T
** e"..." : Escape sequences
? e"This is\na string\nformatted by\nEscape sequences \x21
/* The result :
This is
a string
formatted by
Escape sequences !
*/
@ MAXROW(), 0 WAIT "EOF DTS_Exts.prg" RETURN // DTS_Exts.Main() *~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~