Tag Archives: Script File
xBase File Types
xBase File Types and Extensions
| Ext. | File Type | Introduced or used by |
| .$$$ | temporary file | dBASE III |
| .$db | temporary file | dBASE IV |
| .act | FoxDoc Action Diagrams | FoxPro |
| .app | application object file | dBASE Appl. Generator |
| .app | generated application | FoxPro |
| .bak | Backup file | dBASE |
| .bar | horizontal bar menu object file | dBASE Appl. Generator |
| .bin | Binary files | dBASE |
| .bch | batch process object file | dBASE Appl. Generator |
| .cac | executable when caching on/off | dBASE IV |
| .cat | catalog | dBASE III, IV |
| .cdx | compound index | FoxPro |
| .ch | header file | Clipper |
| .cht | interface file for ChartMaster | dBASE |
| .clp | compiler script file (clip list) | Clipper |
| .cmd | command | dBASE – Waffle |
| .cod | template source file | dBASE Appl. Generator |
| .cpt | encrypted memo file | dBASE |
| .crp | encrypted database | dBASE IV |
| .ctl | control file | dBASE IV – Aldus Setup |
| .cvt | backup file for CONVERTed database file | dBASE IV |
| .db | configuration | dBASE |
| .db$ | temporary file | dBASE |
| .db2 | database | dBASE II |
| .db3 | database | dBASE III |
| .dbf | database file | dBASE – FoxPro |
| .dbk | database backup | dBASE IV |
| .dbo | compiled program | dBASE IV |
| .dbt | FoxBASE+ style memo | FoxPro |
| .dbt | memo file for database w/same name | dBASE – Clipper |
| .def | Definitions list | dBASE |
| .dif | Data Interchange Format. For APPEND FROM, COPY | dBASE – VisiCal |
| .doc | Documentation text file | dBASE Appl. Generator |
| .fil | files list object file | dBASE Appl. Generator |
| .fky | macro file | FoxPro |
| .fmo | compiled format file | dBASE IV |
| .fmt | format file | dBASE – FoxPro – Clipper |
| .fp | configuration file | FoxPro |
| .fpc | catalog | FoxPro |
| .fpt | memo | FoxPro |
| .fr3 | renamed dBASE III+ form file | dBASE IV |
| .frg | uncompiled report file, code fragment file | dBASE IV |
| .frm | report file | dBASE – Clipper |
| .fro | compiled report file | dBASE IV |
| .frt | report memo | FoxPro |
| .frx | report | FoxPro |
| .fw2 | Framework spreadsheet or database file | Framework – dBASE |
| .fxp | compiled format | FoxPro |
| .gen | compiled template | dBASE Appl. Generator |
| .idx | index (many) | FoxPro |
| .ind | include index | dBASE IV |
| .inx | index | FoxBase |
| .key | Key macro library | dBASE |
| .lbg | label generator data | dBASE IV |
| .lbl | label | dBASE – Clipper |
| .lbo | compiled label | dBASE IV |
| .lbt | label memo | FoxPro |
| .lbx | label | FoxPro |
| .ld1 | overlay file | dBASE |
| .log | Transaction log file | dBASE |
| .mbk | multiple index file backup | dBASE IV |
| .mdx | multiple index file | dBASE IV |
| .mem | memory variable save file | dBASE – FoxPro |
| .mnt | menu memo | FoxPro |
| .mnx | menu | FoxPro |
| .mpr | generated program | FoxPro |
| .mpx | compiled menu program | FoxPro |
| .ndx | index file | dBASE |
| .npi | source for DGEN.EXE interpreter | dBASE Appl. Generator |
| .ntx | index file | Clipper |
| .pjt | project memo | FoxPro |
| .pjx | project | FoxPro |
| .plb | library | FoxPro |
| .pll | pre-linked library | Clipper |
| .plt | pre-linked transfer file | Clipper |
| .pop | pop-up menu object | dBASE Appl. Generator |
| .ppo | pre-processor output | Clipper |
| .pr2 | printer driver | dBASE IV |
| .pr3 | PostScript printer driver | dBASE IV |
| .prf | printer driver | dBASE IV |
| .prg | program source file | dBASE – FoxPro – Clipper |
| .prs | procedure | dBASE IV |
| .prt | Print dump | dBASE |
| .prx | compiled program | FoxPro |
| .qbe | saved query (Query By Example) | dBASE IV – Quattro Pro |
| .qbo | compiled query | dBASE IV |
| .qpr | generated query program | FoxPro |
| .qpx | compiled query program | FoxPro |
| .qry | query | dBASE IV |
| .res | dBASE resources | dBASE IV |
| .rpd | Rapid file. For IMPORT/EXPORT,APPEND FROM, COPY | dBASE |
| .sc3 | renamed dBASE III screen mask file | dBASE IV |
| .scr | screen – screen snapshot | dBASE IV |
| .sct | screen memo | FoxPro |
| .scx | screen | FoxPro |
| .spr | generated screen program | FoxPro |
| .spx | compiled screen program | FoxPro |
| .str | structure list object file | dBASE Appl. Generator |
| .t44 | Temporary file for Sort or Index | dBASE IV |
| .tbk | memo backup | dBASE IV – FoxPro |
| .tvf | table view settings | dBASE |
| .upd | update data | dBASE |
| .upo | compiled update data | dBASE |
| .val | values list object file | dBASE Appl. Generator |
| .vew | view file | Clipper, Lotus Approach |
| .vue | view | dBASE IV – FoxPro |
| .w44 | temporary file for Sort or Index | dBASE |
| .wfm | form object | dBASE Form Designer |
| .win | window file | FoxPro – dBASE |
Source : http://www.clicketyclick.dk/databases/xbase/format/index.html
Notes:
– Such a list can’t be perfect. Some item may be obsolete / forgotten and something may not exist when this list compiled.
– “Clipper” may not include all versions of Clipper.
– Most of Clipper files are supported by Harbour.
HbRun
HbRun is a console interpreter and program ( command file / script file / .prg / .hrb ) runner for the Harbour Language.
Addendum: a clarification by Przemek:
HBRUN is a simple wrapper to Harbour compiler so the same syntax as in
Cl*pper is supported:
DO <filename>[.prg]
only .prg is accepted as extension and it’s default so you do not
have to set it explicitly.
( In Harbour Users Google group, under “hbmk2 and the Dot Prompt” topic:
It can work as interpreter when invoked without parameters or can execute xBase / Harbour source code in .prg file or compiled Harbour Portable Objects (.hrb) file given as parameter.
Type of file is recognized by extension used with <file> parameter. If not given then .hrb is used.
In other words, HbRun can be use in both interpret and batch mode.
Regarding parameter given or not, when calling HbRun this ‘mode’ determined by program itself. If a parameter ( usually a .prg or .hrb file name ) given, program run in ‘batch’ mode, runs (executes) given script file and end. If no parameter given, program enter interpreter mode.
Using HbRun as an interpreter, may be very useful, productive, and educative for xBase programmers. Too many xBase programmers was learned everything, including DBF file system and xBase programming language by famous “dot prompt”. Today many xBase programmers uses HbRun daily basis.
When HbRun begin, open a console screen with two basic area: status bars at top and dot prompt line at bottom.
Status bars :
Dot prompt is quite simple visually: a dot and a line in inverse color beginning with a blinking cursor :
You may enter here a command to see the result.
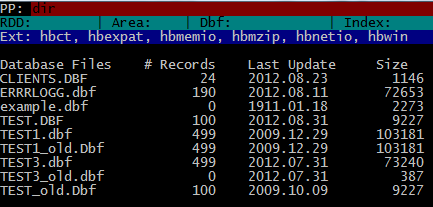
For example “DIR” command will give a list of database (.dbf) files in current directory:
SET COLO TO “GR+/N” command will remember you old days :
The DIR command can be used with DOS style “filter / skeleton” parameter :
DIR *.PRG
DIR *.*
etc.
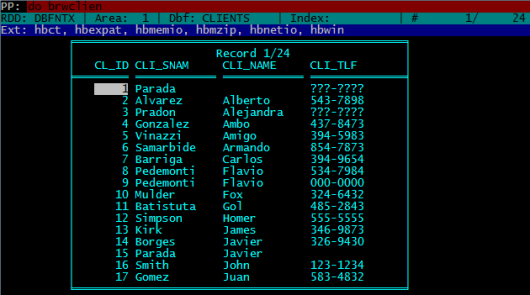
Inspecting any table ( .dbf file ) is very simple:
USE CLIENTS
BROWSE ()
Expand a little:
SET COLO TO “GB+/N”
USE CLIENTS
BROWSE( 3, 10, 24, 60 )
If you plan to use this snap frequently, make a .prg file (say brwclien.prg) with this three line and run it with DO command:
DO BRWCLIEN
Sometime LIST command may be better:
LIST CL_ID, CLI_SNAM, CLI_NAME, CLI_TLF
You can add FOR clause to the LIST command:
LIST CL_ID, CLI_SNAM, CLI_NAME, CLI_TLF FOR RECN() < 10
or
LIST CL_ID, CLI_SNAM, CLI_NAME, CLI_TLF FOR EMPTY( CLI_TLF )
The structure info of a table frequently requires while daily work to xBase Programmers.
Here three small programs for obtain structure info of a table. Usage is quite simple: open ( USE ) your table and enter DO <prgFileName>; for example:
USE CLIENT
DO LISTSTRU
or
DO DISPSTRU
or
DO SAVESTRU
Notes :
– To avoid some possible screen metric conflicts caused by default console (DOS box) settings of OS, may be useful some adjusting before invoke HbRun; such as:
MODE CON LINES=48 COLS=128
– “?” command may be useful as a built-in calculator :
? 2*2 // 4
? 2**8 // 256
? SQRT( 81 ) // 9
– HbRun keep a “history” for commands entered (for a limited count of commands of course). You can access (and re-enter when required) by using up and down keys. Moreover this history may be usable after re-invoke HbRun.
– Though Harbour Language is essential, some legal Harbour commands / functions may be un-recognizable by HbRun.
– Though some legal statements works in interpret mode, may not works in batch mode (such as Browse() ).
Last Note : No further explanation required for experienced xBase programmers; try, see and learn.
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
Examples :
/*
DispStru.prg
Display structure of current table ( .dbf file ) on screen.
*/
MEMVAR ASTRUCT, NTOTLEN
IF EMPTY( ALIAS() )
SETCOLOR( "R/N" )
? "No active table in the current work area !", LTRIM( STR( SELECT() ) )
ELSE
@ 3, 0 CLEA TO MAXROW() - 1, MAXCOL()
aStruct := DBSTRUCT()
nTotLen := 1
AEVAL( aStruct, { | a1Field | nTotLen += a1Field[ 3 ] } )
AEVAL( aStruct, { | a1Field, n1FieldNo | ;
aStruct[ n1FieldNo ] := STR( n1FieldNo, 3 ) + " " +;
PADR( a1Field[ 1 ], 12 ) +;
PADC( a1Field[ 2 ], 4 ) +;
PADL( a1Field[ 3 ], 5 ) +;
PADL( a1Field[ 4 ], 3 ) } )
? "Structure of database :", DBINFO( 10 )
? "Number of data records :", LTRIM( STR( LASTREC() ) )
? "Date of last update :", LUPDATE()
? "Fld Name Type Width Dec"
? "--- ---------- ---- ----- ---"
@ 21,0 SAY "** Total ** " + PADL( nTotLen, 6 )
ACHOICE( 8, 0, 20, 30, aStruct )
ENDIF
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
/*
ListStru.prg
List structure of current table ( .dbf file ) on screen.
*/
MEMVAR ASTRUCT, NTOTLEN
IF EMPTY( ALIAS() )
SETCOLOR( "R/N" )
? "No active table in the current work area !", LTRIM( STR( SELECT() ) )
ELSE
@ 3, 0 CLEA TO MAXROW() - 1, MAXCOL()
aStruct := DBSTRUCT()
nTotLen := 1
AEVAL( aStruct, { | a1Field | nTotLen += a1Field[ 3 ] } )
AEVAL( aStruct, { | a1Field, n1FieldNo | ;
aStruct[ n1FieldNo ] := STR( n1FieldNo, 3 ) + " " +;
PADR( a1Field[ 1 ], 12 ) +;
PADC( a1Field[ 2 ], 4 ) +;
PADL( a1Field[ 3 ], 5 ) +;
PADL( a1Field[ 4 ], 3 ) } )
? "Structure of database :", DBINFO( 10 )
? "Number of data records :", LTRIM( STR( LASTREC() ) )
? "Date of last update :", LUPDATE()
? "Fld Name Type Width Dec"
? "--- ---------- ---- ----- ---"
AEVAL( aStruct, { | c1Field | QOUT( c1Field ) } )
? "** Total ** ", PADL( nTotLen, 5 )
ENDIF
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
/*
SaveStru.prg
Save structure of current table ( .dbf file ) to a file.
Notes :
- This program uses ListStru.prg
- Name of target file constructed at line 18;
if required you may use alternate ways or
simply using a constant.
*/
MEMVAR AlteFName
IF EMPTY( ALIAS() )
SETCOLOR( "R/N" )
? "No active table in the current work area !", LTRIM( STR( SELECT() ) )
ELSE
AlteFName := LEFT( ALIAS(), 4 ) + "STRU"
SET ALTE TO &AlteFName
SET ALTE ON
DO LISTSTRU
SET ALTE OFF
SET ALTE TO
ENDIF
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
Configuration Terms
Application :
A program designed to execute a set of interrelated tasks. Typically referring to a system designed to address a particular business purpose (e.g., Order Entry/Inventory/Invoicing, a document tracking database, or an insurance claims calculator).
Environment Variables :
Operating system variables that can be used to communicate configuration information to executable programs. Environment variables are manipulated using the DOS SET command. The Clipper language compiler and linker respond to certain environment variables. Clipper programs can inspect the settings of environment variables using the GETENV() function.
Executable File :
A file output from the linker directly executable from the operating system command line. Executable files have an .EXE extension.
See Also: Linker
Header File :
A source file containing manifest constant definitions; command or pseudofunctions; and/or program statements merged into another source file using the #include preprocessor directive.
See Also: Program File, Source Code, STD.CH
Library File :
A file containing one or more object modules. The linker searches specified libraries to resolve references to functions or procedures that were not defined in the object files being linked.
See Also: Linker, Module, Object File
Make File :
A text file used as input to a make utility containing the specifications and actions required to build a program or a system of programs. This file is often referred to as a description file.
See Also: Make
Object File :
A file that contains the output of a compiler or other language translator, generally the result of compiling a single source file. Object files are linked to create an executable program.
See Also: Linking, Program File
Procedure File :
An ASCII text file containing Clipper language procedure and function definitions usually ending with a (.prg) extension; a program file.
See Also: Program File
Program File :
An ASCII text file containing Clipper language source code. Program files usually end with a (.prg) extension. The compiler reads the program file, translates the source code, and produces an object file, that is then linked to produce an executable program.
See Also: Linking Object File Source Code
Script File :
A text file that contains command input to a compiler, linker, or other utility program. A script file is often used in lieu of equivalent keyboard input. For the Clipper compiler, script files contain a list of source files to be compiled into a single object file.
Source File :
A text file including source code.
See Also: Program File, Header File
Debugger Terms
Active Window :
The window to which all keystrokes (except those valid in the Command Window) apply. An active window is indicated by a highlighted border. The Tab and Shift-Tab keys are used to select the next and previous window, respectively.
Animate Mode :
The mode of execution in which an application runs one line at a time until a Breakpoint or Tracepoint is reached, with the Execution Bar moving to each line as it is executed.
Breakpoint :
A point at which an application pauses execution and returns control to the debugger.
Callstack :
A list containing the names of all pending activations at the current point in an application.
Callstack Window :
The window in which the Callstack is displayed.
Code Window :
The window in which source code is displayed.
Command Window :
The window in which commands are displayed and entered.
Cursor :
The cursor indicates the current line and/or column position in the active window or dialog box. Note that some windows, such as the Monitor Window, do not utilize the cursor. When a window that does not utilize the cursor is active, the cursor appears in the Code Window.
See Also: Highlight, Input Focus
Debugger :
A tool used to track down errors in a program.
Dialog Box :
A box displayed from within the debugger whenever further input is required.
Execution Bar :
The highlight bar which is positioned on the line of code to be executed next.
Help Window :
The window in which online help is displayed.
Inspecting :
The process of examining work areas, variables, expressions and activations inside the debugger.
Menu Bar :
The bar at the top of the debugger screen, on which the available menu choices are displayed.
Monitor Window :
The window in which monitored variables are displayed.
Monitored Variable :
A variable which is selected by the options on the Monitor Menu and displayed in the Monitor Window.
Run Mode :
The mode of execution in which an application executes without pausing, until a Breakpoint or Tracepoint is reached.
Script File :
A file in which frequently used debugger commands are stored and from which those commands can be executed.
Set Colors Window :
The window in which the Debugger color settings can be inspected.
Single Step Mode :
The mode of execution in which only the line of code highlighted by the Execution Bar is executed, and its output displayed.
Trace Mode :
A mode of execution similar to Single Step Mode, the difference being that Trace Mode traces over function and procedure calls.
Tracepoint :
A variable or expression whose value is displayed in the Watch Window, and which causes an application to pause whenever that value changes.
View Sets Window :
The window in which Clipper language status settings can be inspected.
View Workareas Window :
The window in which work area information is displayed.
Watch Window :
The window in which Watchpoints and Tracepoints are displayed.
Watchpoint :
A variable or expression whose value is displayed in the Watch Window and updated as an application executes.