Tag Archives: EMPTY()
String Functions
CharAdd
CharAnd
CharEven
CharHist
CharList
CharMirr
CharMix
CharNoList
CharNot
CharOdd
CharOne
CharOnly
CharOr
CharPix
CharRela
CharRelRep
CharRem
CharRepl
CharRLL
CharRLR
CharSHL
CharSHR
CharSList
CharSort
CharSub
CharSwap
CharWin
CharXOR
CountLeft
CountRight
Descend
Empty
hb_At
hb_RAt
hb_ValToStr
IsAlpha
IsDigit
IsLower
IsUpper
NumAt
NumToken
PadLeft
PadRight
POSALPHA
POSCHAR
POSDEL
POSDIFF
POSEQUAL
POSINS
POSLOWER
POSRANGE
POSREPL
POSUPPER
TokenAt
TokenEnd
TokenExit
TokenInit
TokenLower
TokenNext
TokenNum
TokenSep
TokenUpper
Len()
LEN()
Returns size of a string or size of an array.
Syntax
LEN( <cString> | <aArray> ) --> <nLength>
Arguments
<acString> is a character string or the array to check.
Returns
The length of the string or the number of elements that contains an array.
Description
This function returns the string length or the size of an array or the size of a hash table. If it is used with a multidimensional array it returns the size of the first dimension.
Examples
? LEN( "Harbour" ) // 7
? LEN( { "One", "Two" } ) // 2
Tests
PROCEDURE Test()
LOCAL cName := ""
ACCEPT "Enter your name: " TO cName
? LEN( cName )
RETURN
Compliance
Clipper
Files
Library is rtl
Seealso
EMPTY(), RTRIM(), LTRIM(), AADD(), ASIZE()
C5_EMPTY
EMPTY()
Determine if the result of an expression is empty
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Syntax
EMPTY(<exp>) --> lEmpty
Arguments
<exp> is an expression of any data type.
Returns
EMPTY() returns true (.T.) if the expression results in an empty value;
otherwise, it returns false (.F.). The criteria for determining whether
a value is considered empty depends on the data type of <exp> according
to the following rules:
List of Empty Values
------------------------------------------------------------------------
Data Type Contents
------------------------------------------------------------------------
Array Zero-length
Character Spaces, tabs, CR/LF, or ("")
Numeric 0
Date Null (CTOD(""))
Logical False (.F.)
Memo Same as character
NIL NIL
------------------------------------------------------------------------
Description
The EMPTY() function has a number of uses. You can use it to determine
if a user entered a value into a Get object before committing changes to
a database file. It can also determine whether a formal parameter is
NIL or unsupplied. In addition, it can test an array for zero-length.
Notes
. Space characters: The EMPTY() function treats carriage
returns, line feeds, and tabs as space characters and removes these
as well.
Examples
. These examples illustrate use of EMPTY() against several
different data types:
? EMPTY(SPACE(5)), EMPTY("") // Result: .T. .T.
? EMPTY(0), EMPTY(CTOD("")) // Result: .T. .T.
? EMPTY(.F.), EMPTY(NIL) // Result: .T. .T.
. This example uses EMPTY() to determine whether the user
entered a value into the first Get object before writing the new
value to the database file:
LOCAL cCust := SPACE(15), nAmount := 0
USE Sales NEW
@ 10, 10 GET cCust
@ 11, 10 GET nAmount PICTURE "999.99"
READ
//
IF !EMPTY(cCust)
APPEND BLANK
REPLACE Sales->Cust WITH cCust, Sales->Amount ;
WITH nAmount
ENDIF
. This example uses EMPTY() as part of the VALID clause to force
the user to enter data into the current Get object:
LOCAL cCode := SPACE(5)
@ 2, 5 SAY "Enter code" GET cCode VALID !EMPTY(cCode)
READ
Files Library is CLIPPER.LIB.
See Also: LEN()
Hash vs Table
Consider a table for customers records with two character fields : Customer ID and customer name:
| Cust_ID | Cust_Name |
| CC001 | Pierce Firth |
| CC002 | Stellan Taylor |
| CC003 | Chris Cherry |
| CC004 | Amanda Baranski |
It’s known all possible and necessary operations on a table: APPEND, DELETE, SEEK and so on; by the way, for SEEK we need an index file also.
Listing this table is quite simple:
USE CUSTOMER
WHILE .NOT. EOF()
? CUST_ID, CUST_NAME
DBSKIP()
ENDDO
If our table is sufficiently small, we can find a customer record without index and SEEK :
LOCATE FOR CUST_ID = “CC003”
? CUST_ID, CUST_NAME
If we want all our data will stand in memory and we could manage it more simple and quick way, we would use an array ( with some considerations about size of table; if it is too big, this method will be problematic ) :
aCustomer := {} // Declare / define an empty array
USE CUSTOMER
WHILE .NOT. EOF()
AADD(aCustomer, { CUST_ID, CUST_NAME } )
DBSKIP()
ENDDO
Traversing this array is quite simple :
FOR nRecord := 1 TO LEN( aCustomer )
? aCustomer[ nRecord, 1 ], aCustomer[ nRecord, 2 ]
NEXT
or :
a1Record := {}
FOR EACH a1Record IN aCustomer
? a1Record[ 1 ], a1Record[ 2 ]
NEXT
And locating a specific record too:
nRecord := ASCAN( aCustomer, { | a1Record | a1Record[ 1 ] == “CC003” } )
? aCustomer[ nRecord, 1 ], aCustomer[ nRecord, 2 ]
A lot of array functions are ready to use for maintain this array : ADEL(), AADD(), AINS() etc …
Now, let’s see how we could use a hash for achieve this job :
hCustomer := { => } // Declare / define an empty hash
USE CUSTOMER
WHILE .NOT. EOF()
hCustomer[ CUST_ID ] := CUST_NAME
DBSKIP()
ENDDO
Let’s traversing :
h1Record := NIL
FOR EACH h1Record IN hCustomer
? h1Record: __ENUMKEY(),h1Record:__ENUMVALUE()
NEXT
Now, we have a bit complicate our job; a few field addition to the table :
| No: | Field Name | Type | Width | Dec | Decription |
|
1 |
CUST_ID |
C |
5 |
0 |
Id ( Code ) |
|
2 |
CUST_NAME |
C |
10 |
0 |
Name |
|
3 |
CUST_SNAM |
C |
10 |
0 |
Surname |
|
4 |
CUST_FDAT |
D |
8 |
0 |
First date |
|
5 |
CUST_ACTV |
L |
1 |
0 |
Is active ? |
|
6 |
CUST_BLNCE |
N |
11 |
2 |
Balance |
While <key> part of an element of a hash may be C / D / N / L type; <xValue> part of hash too may be ANY type of data, exactly same as arrays.
So, we can make fields values other than first ( ID) elements of an array:
hCustomer := { => } // Declare / define an empty hash
USE CUSTOMER
WHILE .NOT. EOF()
a1Data:= { CUST_NAME, CUST_SNAM, CUST_FDAT, CUST_ACTV, CUST_BLNCE }
hCustomer[ CUST_ID ] := a1Data
DBSKIP()
ENDDO
Let’s traversing :
h1Record := NIL
FOR EACH h1Record IN hCustomer
a1Key := h1Record:__ENUMKEY()
a1Data := h1Record:__ENUMVALUE()
? a1Key
AEVAL( a1Data, { | x1 | QQOUT( x1 ) } )
NEXT
*-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._
/*
Hash vs Tables
*/
#define NTrim( n ) LTRIM( STR( n ) )
#define cLMarj SPACE( 3 )
PROCEDURE Main()
SET DATE GERM
SET CENT ON
SET COLO TO "W/B"
SetMode( 40, 120 )
CLS
hCustomers := { => } // Declare / define an empty PRIVATE hash
IF MakUseTable()
Table2Hash()
* Here the hash hCustomers may be altered in any way
ZAP
Hash2Table()
ELSE
? "Couldn't make / USE table"
ENDIF
?
@ MAXROW(), 0
WAIT "EOF HashVsTable.prg"
RETURN // HashVsTable.Main()
*-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.
PROCEDURE Table2Hash()
hCustomers := { => }
WHILE .NOT. EOF()
hCustomers[ CUST_ID ] := CUST_SNAM
DBSKIP()
ENDDO
ListHash( hCustomers, "A hash transferred from a table (single value)" )
hCustomers := { => } // Declare / define an empty hash
DBGOTOP()
WHILE .NOT. EOF()
hCustomers[ CUST_ID ] := { CUST_NAME, CUST_SNAM, CUST_FDAT, CUST_ACTV, CUST_BLNCE }
DBSKIP()
ENDDO
ListHash( hCustomers, "A hash transferred from a table (multiple values)" )
RETURN // Table2Hash()
*-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.
PROCEDURE Hash2Table()
LOCAL h1Record,;
c1Key,;
a1Record,;
n1Field
FOR EACH h1Record IN hCustomers
c1Key := h1Record:__ENUMKEY()
a1Record := h1Record:__ENUMVALUE()
DBAPPEND()
FIELDPUT( 1, c1Key )
AEVAL( a1Record, { | x1, n1 | FIELDPUT( n1 + 1 , x1 ) } )
NEXT h1Record
DBGOTOP()
?
? "Data trasferred from hash to table :"
?
WHILE ! EOF()
? STR( RECN(), 5), ''
FOR n1Field := 1 TO FCOUNT()
?? FIELDGET( n1Field ), ''
NEXT n1Field
DBSKIP()
ENDDO
RETURN // Hash2Table()
*-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.
PROCEDURE ListHash( hHash, cComment )
LOCAL x1Pair
cComment := IF( HB_ISNIL( cComment ), '', cComment )
?
? cComment // , "-- Type :", VALTYPE( hHash ), "size:", LEN( hHash )
?
IF HB_ISHASH( hHash )
FOR EACH x1Pair IN hHash
nIndex := x1Pair:__ENUMINDEX()
x1Key := x1Pair:__ENUMKEY()
x1Value := x1Pair:__ENUMVALUE()
? cLMarj, NTrim( nIndex )
* ?? '', VALTYPE( x1Pair )
?? '', x1Key, "=>"
* ?? '', VALTYPE( x1Key )
* ?? VALTYPE( x1Value )
IF HB_ISARRAY( x1Value )
AEVAL( x1Value, { | x1 | QQOUT( '', x1 ) } )
ELSE
?? '', x1Value
ENDIF
NEXT
ELSE
? "Data type error; Expected hash, came", VALTYPE( hHash )
ENDIF HB_ISHASH( hHash )
RETURN // ListHash()
*-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.
FUNCTION MakUseTable() // Make / USE table
LOCAL cTablName := "CUSTOMER.DBF"
LOCAL lRetval, aStru, aData, a1Record
IF FILE( cTablName )
USE (cTablName)
ELSE
aStru := { { "CUST_ID", "C", 5, 0 },;
{ "CUST_NAME", "C", 10, 0 },;
{ "CUST_SNAM", "C", 10, 0 },;
{ "CUST_FDAT", "D", 8, 0 },;
{ "CUST_ACTV", "L", 1, 0 },;
{ "CUST_BLNCE", "N", 11, 2 } }
*
* 5-th parameter of DBCREATE() is alias -
* if not given then WA is open without alias
* ^^^^^^^^^^^^^
DBCREATE( cTablName, aStru, , .F., "CUSTOMER" )
aData := { { "CC001", "Pierce", "Firth", 0d20120131, .T., 150.00 },;
{ "CC002", "Stellan", "Taylor", 0d20050505, .T., 0.15 },;
{ "CC003", "Chris", "Cherry", 0d19950302, .F., 0 },;
{ "CC004", "Amanda", "Baranski", 0d20011112, .T., 12345.00 } }
FOR EACH a1Record IN aData
CUSTOMER->(DBAPPEND())
AEVAL( a1Record, { | x1, nI1 | FIELDPUT( nI1, X1 ) } )
NEXT a1Record
DBGOTOP()
ENDIF
lRetval := ( ALIAS() == "CUSTOMER" )
RETURN lRetval // MakUseTable()
*-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._

Operator overloading
/*
Operator overloading
Some operators overloaded by extending their functionalities.
"$" was an operator for "checking substring existence in a string"
For example :
? "A" $ "ABC" // Result: .T.
? "Z" $ "ABC" // Result: .F.
Now, this operator can be used for arrays and hashs too, not only strings.
See examples below.
"=>" was a preprocessor operator with meaning "translate to : ...".
Now, this operator can be used as a <key> - <value> separator in Hashs
for define and / or assign <key> - <value> to Hashs.
See examples below.
"[ ]" was Array element indicator (Special)
"{ }" was Literal array and code block delimiters (Special)
Now, this indicators can be used for hashs too.
See examples below.
"+=" is self-increment operator that can be used both numeric
and string values.
Such as :
cTest := "This"
cTest += " is"
? cTest // This is
nTest := 3
nTest += 10
? nTest // 13
Now, this operator can be used for adding elements to an existing hash;
( but no for arrays ! ).
Note : Extended functionalities of $ and += operators depends xHB lib.
So need this usages to xHB lib and xHB.ch.
See examples below.
*/
#include "xhb.ch"
PROCEDURE Main()
CLS
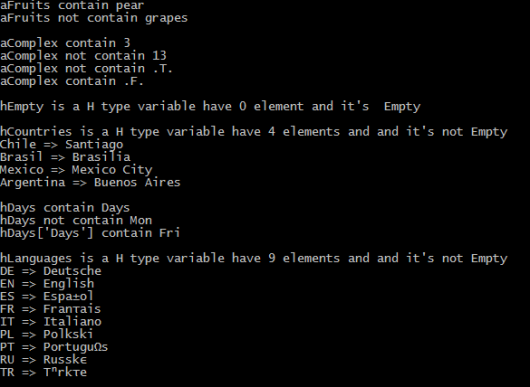
aFruits := { "apple", "appricot", "cherry", "melon", "pear", "mulberry" }
? "aFruits", IF( "pear" $ aFruits, '', 'not ' ) + "contain pear"
? "aFruits", IF( "grapes" $ aFruits, '', 'not ' ) +"contain grapes"
aComplex := ARRAY( 10 )
AEVAL( aComplex, { | x1, i1 | aComplex[ i1 ] := i1 } )
aComplex[ 5 ] := DATE()
aComplex[ 7 ] := .F.
?
? "aComplex", IF( 3 $ aComplex, '', 'not ' ) + "contain 3"
? "aComplex", IF( 13 $ aComplex, '', 'not ' ) + "contain 13"
? "aComplex", IF( .T. $ aComplex, '', 'not ' ) + "contain .T."
? "aComplex", IF( .F. $ aComplex, '', 'not ' ) + "contain .F."
hEmpty := { => }
?
? "hEmpty is a", VALTYPE( hEmpty ), "type variable have",;
STR( LEN( hEmpty ), 1 ), "element and it's",;
IF( EMPTY( hEmpty ), '', 'not' ), "Empty"
hCountries := { 'Argentina' => "Buenos Aires" }
hCountries += { 'Brasil' => "Brasilia" }
hCountries += { 'Chile' => "Santiago" }
hCountries += { 'Mexico' => "Mexico City" }
?
? "hCountries is a", VALTYPE( hCountries ), "type variable have",;
STR( LEN( hCountries ), 1 ), "elements and and it's",;
IF( EMPTY( hCountries ), '', 'not' ), "Empty"
cCountry := NIL
FOR EACH cCountry IN hCountries
? cCountry:__ENUMKEY(), "=>", cCountry:__ENUMVALUE()
NEXT
hDays := { 'Days' => { "Mon", "Tue", "Wed", "Thu", "Fri", "Sat", "Sun" } }
?
? "hDays", IF( 'Days' $ hDays, '', 'not ' ) + "contain Days"
? "hDays", IF( "Mon" $ hDays, '', 'not ' ) + "contain Mon"
? "hDays['Days']", IF( "Fri" $ hDays["Days"], '', 'not ' ) + "contain Fri"
hLanguages := { "EN" => "English" } +;
{ "DE" => "Deutsche" } +;
{ "ES" => "Español" } +;
{ "FR" => "Français" } +;
{ "IT" => "Italiano" } +;
{ "PL" => "Polkski" } +;
{ "PT" => "Português" } +;
{ "RU" => "Russkî" } +;
{ "TR" => "Türkçe" }
?
? "hLanguages is a", VALTYPE( hLanguages ), "type variable have",;
STR( LEN( hLanguages ), 1 ), "elements and and it's",;
IF( EMPTY( hLanguages ), '', 'not' ), "Empty"
cLanguage := NIL
FOR EACH cLanguage IN hLanguages
? cLanguage:__ENUMKEY(), "=>", cLanguage:__ENUMVALUE()
NEXT
@ MAXROW(), 0
WAIT "EOF OprOLoad.prg"
RETURN // OprOLoad.Prg.Main()
C5 Data Manipulation Functions
Array :
AADD() :
Add a new element to the end of an array
AADD( <aTarget>, <expValue> ) --> Value
ACLONE() :
Duplicate a nested or multidimensional array
ACLONE( <aSource> ) --> aDuplicate
ACOPY() :
Copy elements from one array to another
ACOPY( <aSource>, <aTarget>, [ <nStart> ], [ <nCount> ],
[ <nTargetPos> ] ) --> aTarget
ADEL() :
Delete an array element
ADEL( <aTarget>, <nPosition> ) --> aTarget
ADIR()* :
Fill a series of arrays with directory information
ADIR([ <cFilespec> ],
[ <aFilenames> ],
[ <aSizes> ],
[ <aDates> ],
[ <aTimes> ],
[ <aAttributes> ] ) --> nFiles
AEVAL() :
Execute a code block for each element in an array
AEVAL( <aArray>, <bBlock>, [ <nStart> ], [ <nCount> ] ) --> aArray
AFILL() :
Fill an array with a specified value
AFILL( <aTarget>, <expValue>, [ <nStart> ], [ <nCount> ] )
--> aTarget
AINS() :
Insert a NIL element into an array
AINS( <aTarget>, <nPosition> ) --> aTarget
ARRAY() :
Create an uninitialized array of specified length
ARRAY( <nElements> [, <nElements>...] ) --> aArray
ASCAN() :
Scan an array for a value or until a block returns (.T.)
ASCAN( <aTarget>, <expSearch>, [ <nStart> ], [ <nCount> ] )
--> nStoppedAt
ASIZE() :
Grow or shrink an array
ASIZE( <aTarget>, <nLength> ) --> aTarget
ASORT() :
Sort an array
ASORT( <aTarget>, [ <nStart> ], [ <nCount> ], [ <bOrder> ] )
--> aTarget
ATAIL() :
Return value of the highest numbered (last) element of an array
ATAIL( <aArray> ) --> Element
Common :
EMPTY() :
Determine if the result of an expression is empty
EMPTY( <exp> ) --> lEmpty
LEN() :
Return the length of a character string or array size
LEN( <cString> | <aArray> ) --> nCount
MAX() :
Return the larger of two numeric or date values
MAX( <nExp1>, <nExp2> ) --> nLarger MAX( <dExp1>, <dExp2> ) --> dLarger
MIN() :
Return the smaller of two numeric or date values
MIN( <nExp1>, <nExp2> ) --> nSmaller MIN( <dExp1>, <dExp2> ) --> dSmaller
PAD() :
Pad character, date or numeric values with a fill character
PADL( <exp>, <nLength>, [ <cFillChar> ] ) --> cPaddedString PADC( <exp>, <nLength>, [ <cFillChar> ] ) --> cPaddedString PADR( <exp>, <nLength>, [ <cFillChar> ] ) --> cPaddedString
TRANSFORM() :
Convert any value into a formatted character string
TRANSFORM( <exp>, <cSayPicture> ) --> cFormatString
TYPE() :
Determine the type of an expression
TYPE( <cExp> ) --> cType
VALTYPE() :
Determine the data type returned by an expression
VALTYPE( <exp> ) --> cType
Date & Time :
CDOW() :
Convert a date value to a character day of the week
CDOW( <dExp> ) --> cDayName
CMONTH() :
Convert a date to a character month name
CMONTH( <dDate> ) --> cMonth
CTOD() :
Convert a date string to a date value
CTOD( <cDate> ) --> dDate
DATE() :
Return the system date as a date value
DATE() --> dSystem
DAY() :
Return the day of the month as a numeric value
DAY( <dDate> ) --> nDay
DOW() :
Convert a date value to a numeric day of the week
DOW( <dDate> ) --> nDay
DTOC() :
Convert a date value to a character string
DTOC( <dDate> ) --> cDate
DTOS() :
Convert a date value to a string formatted as yyyymmdd
DTOS( <dDate> ) --> cDate
MONTH() :
Convert a date value to the number of the month
MONTH( <dDate> ) --> nMonth
SECONDS() :
Return the number of seconds elapsed since midnight
SECONDS() --> nSeconds
TIME() :
Return the system time
TIME() --> cTimeString
YEAR() :
Convert a date value to the year as a numeric value
YEAR( <dDate> ) --> nYear
Numeric :
ABS() :
Return the absolute value of a numeric expression
ABS( <nExp> ) --> nPositive
BIN2I() :
Convert a 16-bit signed integer to a numeric value
BIN2I( <cSignedInt> ) --> nNumber
BIN2L() :
Convert a 32-bit signed integer to a numeric value
BIN2L( <cSignedInt> ) --> nNumber
BIN2W() :
Convert a 16-bit unsigned integer to a numeric value
BIN2W( <cUnsignedInt> ) --> nNumber
EXP() :
Calculate e**x
EXP( <nExponent> ) --> nAntilogarithm
INT() :
Convert a numeric value to an integer
INT( <nExp> ) --> nInteger
I2BIN() :
Convert a numeric to a 16-bit binary integer
I2BIN( <nInteger> ) --> cBinaryInteger
LOG() :
Calculate the natural logarithm of a numeric value
LOG( <nExp> ) --> nNaturalLog
L2BIN() :
Convert a numeric value to a 32-bit binary integer
L2BIN( <nExp> ) --> cBinaryInteger
MOD()* :
Return dBASE III PLUS modulus of two numbers
MOD( <nDividend>, <nDivisor> ) --> nRemainder
ROUND() :
Return a value rounded to a specified number of digits
ROUND( <nNumber>, <nDecimals> ) --> nRounded
SQRT() :
Return the square root of a positive number
SQRT( <nNumber> ) --> nRoot
VAL() :
Convert a character number to numeric type
VAL( <cNumber> ) --> nNumber
String & Memo :
ALLTRIM() :
Remove leading and trailing spaces from character string
ALLTRIM( <cString> ) --> cTrimString
ASC() :
Convert a character to its ASCII value
ASC( <cExp> ) --> nCode
AT() :
Return the position of a substring within a string
AT( <cSearch>, <cTarget> ) --> nPosition
CHR() :
Convert an ASCII code to a character value
CHR( <nCode> ) --> cChar
HARDCR() :
Replace all soft CRs with hard CRs
HARDCR( <cString> ) --> cConvertedString
ISALPHA() :
Determine if the leftmost character is alphabetic
ISALPHA( <cString> ) --> lBoolean
ISDIGIT() :
Determine if the leftmost character is a digit
ISDIGIT( <cString> ) --> lBoolean
ISLOWER() :
Determine if the leftmost character is a lower case letter
ISLOWER( <cString> ) --> lBoolean
ISUPPER() :
Determine if the leftmost character is upper case
ISUPPER( <cString> ) --> lBoolean
LEFT() :
Extract a substring beginning with the first character
LEFT( <cString>, <nCount> ) --> cSubString
LOWER() :
Convert uppercase characters to lowercase
LOWER( <cString> ) --> cLowerString
LTRIM() :
Remove leading spaces from a character string
LTRIM( <cString> ) --> cTrimString
MEMOEDIT() :
Display or edit character strings and memo fields
MEMOEDIT( [ <cString> ],
[ <nTop> ], [ <nLeft> ],
[ <nBottom> ], [ <nRight> ],
[ <lEditMode> ],
[ <cUserFunction> ],
[ <nLineLength> ],
[ <nTabSize> ],
[ <nTextBufferRow> ],
[ <nTextBufferColumn> ],
[ <nWindowRow> ],
[ <nWindowColumn> ] ) --> cTextBuffer
MEMOLINE() :
Extract a line of text from character string or memo field
MEMOLINE( <cString>,
[ <nLineLength> ],
[ <nLineNumber> ],
[ <nTabSize> ],
[ <lWrap> ] ) --> cLine
MEMOREAD() :
Return the contents of a disk file as a character string
MEMOREAD( <cFile> ) --> cString
MEMOTRAN() :
Replace carriage return/line feeds in character strings
MEMOTRAN( <cString>,
[ <cReplaceHardCR> ],
[ <cReplaceSoftCR> ] ) --> cNewString
MEMOWRIT() :
Write a character string or memo field to a disk file
MEMOWRIT( <cFile>, <cString> ) --> lSuccess
MLCOUNT() :
Count the lines in a character string or memo field
MLCOUNT( <cString>, [ <nLineLength> ], [ <nTabSize> ],
[ <lWrap> ] ) --> nLines
MLCTOPOS() :
Return byte position based on line and column position
MLCTOPOS( <cText>, <nWidth>, <nLine>,
<nCol>, [ <nTabSize> ], [ <lWrap> ] ) --> nPosition
MLPOS() :
Determine the position of a line in a memo field
MLPOS( <cString>, <nLineLength>,
<nLine>, [ <nTabSize> ], [ <lWrap> ] ) --> nPosition
MPOSTOLC() :
Return line and column position based on byte position
MPOSTOLC( <cText>, <nWidth>, <nPos>,
[ <nTabSize> ], [ <lWrap> ] ) --> aLineColumn
RAT() :
Return the position of the last occurrence of a substring
RAT( <cSearch>, <cTarget> ) --> nPosition
REPLICATE() :
Return a string repeated a specified number of times
REPLICATE( <cString>, <nCount> ) --> cRepeatedString
RIGHT() :
Return a substring beginning with rightmost character
RIGHT( <cString>, <nCount> ) --> cSubString
RTRIM() :
Remove trailing spaces from a character string
RTRIM( <cString> ) --> cTrimString
SET EXACT* :
Toggle exact matches for character strings
SET EXACT on | OFF | <xlToggle>
SOUNDEX() :
Convert a character string to soundex form
SOUNDEX( <cString> ) --> cSoundexString
SPACE() :
Return a string of spaces
SPACE( <nCount> ) --> cSpaces
STR() :
Convert a numeric expression to a character string
STR( <nNumber>, [ <nLength> ], [ <nDecimals> ] ) --> cNumber
STRTRAN() :
Search and replace characters within a character string
STRTRAN( <cString>, <cSearch>, [ <cReplace> ],
[ <nStart> ], [ <nCount> ] ) --> cNewString
STUFF() :
Delete and insert characters in a string
STUFF( <cString>, <nStart>, <nDelete>, <cInsert> ) --> cNewString
SUBSTR() :
Extract a substring from a character string
SUBSTR( <cString>, <nStart>, [ <nCount> ] ) --> cSubstring
TRIM() :
Remove trailing spaces from a character string
TRIM( <cString> ) --> cTrimString
UPPER() :
Convert lowercase characters to uppercase
UPPER( <cString> ) --> cUpperString