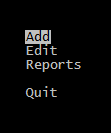Chapter I – Text to text conversion
In Clipper world, “migration” means “convert a DOS based Clipper program to Windows”. This is a dream of every Clipper – DOS programmer.
Before all, we need clarify some terms:
May be found multiple ways for convert a DOS based Clipper program to Windows. In general, DOS programs are runs in “text” mode and Windows program runs in “Graphic” mode; and this is what meant by term “migration”.
Converting a text mode program to directly GUI (Graphical User Interface) is a painful job. First, we need to find a Compiler with GUI support, or a GUI library usable with a specific compiler. If we have more than one opportunity ( yes, it is so ) we need make a choice between them.
For make a right selection we need learn, understand specialties of each option and differences between them.
Believe me, this is an endless way 😦
Instead, let’s begin with simpler thing: convert a DOS text mode program to Windows text mode program.
Question: Without GUI, what meaning will be to migrate from DOS to Windows?
Answer: Good question and like all good question, answer isn’t easy.
First, modern OSs moves away day to day from DOS conditions; memory problems, screen problems, codepage problems, etc… By the time, building / running 16 bit executable becomes more difficult day to day.
Whereas Harbour already is a 32 / 64 bit compiler.
Second, all DOS Compilers for Clipper are commercial and registration required products; furthermore they are almost out of sold for this days; what compiler you could use?
And third, Harbour is best free compiler and the best way to use a free GUI tool for xBase language.
So, beginning with using Harbour in text mode is the best start point, I think.
First step is downloading and install HMG or Harbour. If you didn’t past this step yet please refer previous articles in this section or “Links” page of this blog.
The easiest way for using Harbour compiler is calling hbmk2, the wonderful project maker for Harbour compiler.
Depending your installation, hbmk2 may be in different locations; such as C:\Harbour\bin or c:\hmg\harbour\bin or anything else.
Hereafter I will assume that your hbmk2 is in C:\hmg\Harbour\bin. If your installation is different, please modify above examples.
Second step is assign an empty folder (directory) for work / test affairs; say C:\test.
And the third step is copying your Clipper program(s) to this folder.
But don’t rush; we have some precautions:
– Better way is starting with a single-program project; if you haven’t written a new one. Don’t uses for now projects have multiple program file.
– Your program may have some “national” characters and these characters may be differently shown between DOS and Windows. If so, you may want fix manually these differences via a Windows based text editor. Or use a program if you have one. Harbour has a clever tool (HB_OEMTOANSI() function) is usable for this purpose.
– In Clipper it’s possible a program file without module (procedure / function) definition. If you have such file(s), enclose your code with PROCEDURE — RETURN statement pair.
– Every Harbour project must have one and only one MAIN module (procedure / function). The first procedure / function in your single program file will be considered as MAIN module of your project. (In HMG, name of this module must be “main” also).
– Almost all Clipper commands, statement, functions, pseudo functions, manifest constants etc are usable almost in the same ways with Clipper. May be exist some very few and very rare differences, and of course solving methods for its.
For compile process we will use command box (DOS / console window) of Windows. You can open a console window, with the menu Start -> Run -> cmd or selecting it in the “Command Prompt” from the Start Menu \ All Programs.
– “Command / console window” size may not appropriate for easy use. You may
– use a MODE ( DOS ) command :
MODE CON LINES=54 COLS=148
or
– adding a SetMode() statement at the beginning of MAIN module of your project. For example:
SetMode( 25, 80 ) // 25 line 80 column same as standard
// DOS screen ( but not full screen ! )
SetMode( 48, 128 ) // 48 line 128 column, may be more readable
Now, we are ready to begin: Enter this command in console window :
C:\hmg\harbour\bin hbmk2 <mainPrgName>
You don’t need any SET command (such as PATH etc) before this command; hbmk2 will find all necessary paths / files.
For running executable after compile, add a -run switch to the command line :
C:\hmg\harbour\bin hbmk2 <mainPrgName> -run
Of course, you need supply name of your main .prg file in place of <mainPrgName>.
Note that you don’t need a separate “linking” step; hbmk2 will do everything for you.
You may use this
C:\hmg\harbour\bin hbmk2 <mainPrgName>
command via a batch ( .bat ) command file (such as “build.bat”) too. In this way you can apply compiling process without console window; run .bat file by double click in the Windows Explorer. In this case you may need add a PAUSE command at end of .bat file.
That’s all.
You know, a program file may contains more than one module (procedure / function). So you may develop your project by adding new modules to your single program file.
In this step you don’t need trying extra features, extensions of Harbour. Before that adventure your primary need is to convert existing project Clipper to Harbour.
When you reach a level of multiple-program file project:
– Basic rules are the same: the first module in the your program file is MAIN module of your project.
If your .prg files contains:
SET PROCEDURE TO <procedure_File_Name>
and / or
#include <procedure_File_Name>
you may or may not continue using these statement.
– The shortest way for compiling a multiple-file project is use a .hbp ( Harbour Projet ) file. This is a text file and its simplest form is a file contains list of your .prg files. For example:
myprog01.prg
myprog02.prg
myprog03.prg
myprog04.prg
and the compile command is the same :
C:\hmg\harbour\bin hbmk2 <mainProjectFileName>
In this case you don’t need to use SET PROC… and #include … statement and this is the better way.
Because hbmk2 applies “incremental” compiling, that is compiles only modified files.
Under normal circumstances, any module in any program file is callable in anywhere in the project. If you have some modules that exclusive to this program file, you may use STATIC keyword at the beginning of PROCEDURE / FUNCTION statement. For example:
STATIC FUNCTION OpenTable()
With this syntax you will prevent calling this module outside of this .prg file and the possibility of using this module name into other .prg files.
Example :
Take “A typical Harbour Program” in the “Harbour Sample” page.
As seen at .pdf file by given link, this sample program borrowed from official reference guide of a Clipper compiler. That is, in fact this is a Clipper program and it will may compile with Harbour and run without any modification.
Let’s try.
– Copy and paste this sample and save in your PC with a name say “typical.prg”.
– Comment out the line for now.
#include "Database.prg" // Contains generic database functions
– Call hbmk2:
C:\hmg\harbour\bin hbmk2 typical -run
Note: While working / playing on programs, you may encounter some error messages like:
Error F0029 Can't open #include file xxx
Error E0002 Redefinition of procedure or function xxx
Error: Referenced, missing, but unknown function(s): xxx
undefined reference to HB_FUN_xxx
Please don’t panic !
“Error” is salt and pepper of programming play ! 😉
The worst situation isn’t getting error, but is unable to stay !
The “HB_FUN_xxx” may be seen weird at first meet. The “HB_FUN_” is a prefix given by system ( compiler ) to your function; so you need search erroneous point into tour program files without this prefix.
Now, let’s continue to our “typical” program:
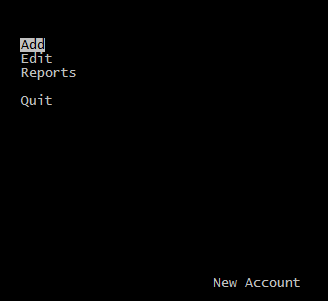
If you compile the program with commented out #include … line, possibly it will work, by opening main menu:
But what’s that?
When selected a menu item (except “Quit”) we can’t see other than an empty screen!
Again, don’t panic!
This situation too is not very rare !
If you use vertical scroll bar of command / console window, you will notice that your screen is considerably much longer than seen !
To avoid this conflict, ( as stated above ) we need use a SetMode() function call at top of our Main() procedure ( but AFTER LOCAL statement ! ) :
SetMode( 24, 79 )
And now everything is OK.
In fact, not really everything, we have a few “fine adjustment”.
Cut and paste the section after “// Database.prg” to a separate “Database.prg” file, un-comment the “#include …” line and then re-compile.
In this case we have a “multiple prg” project. As stated earlier, better way is using a .hbp file instead of “#include …” statements.
Now comment out ( or delete now ) the #include line.
Build a new text file with name “typical.hbp” and with this content :
Typical.prg
DataBase.prg
And recall hbmk2 without any modification :
C:\hmg\harbour\bin hbmk2 typical -run
That’s all !
Congratulations !
Now you have a multiple-prg project !