If a multi-dimension array
– have a fixed number elements in each dimension and
– each column contains the same type of information for each row in array
called “uniform”.
This structure is similar to a table structure.
Built-in functions DBSTRUCT() and DIRECTORY() produces uniform arrays.
Array produced by DBSTRUCT() will have field count in size and the structure of an array is:
Field Name C
Field Type C
Field Width N
Field Dec N
And DIRECTORY() function produces an array with elements as file count and with this structure:
File Name C
File Size N
File Date D
File Time C
File Attributes C
Building, maintaining and using those arrays is simple as possible.
Let’s look at a sample .prg:
-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._
#include "directry.ch"
#include "dbstruct.ch"
PROCEDURE Main()
SET DATE GERM
SET CENT ON
?
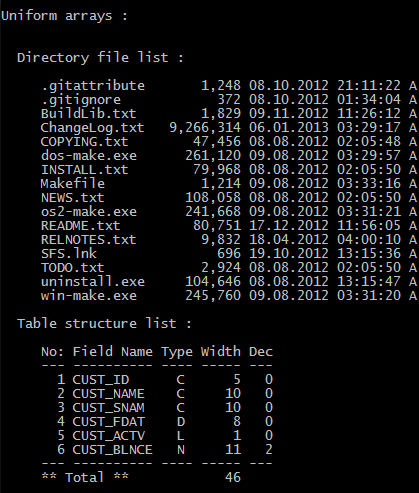
? "Uniform arrays :"
?
?
? " Directory file list :"
?
FileList()
?
? " Table structure list :"
?
IF MakUseTable()
DispStru()
ELSE
? "Couldn't USE or Make th table."
ENDIF
?
@ MAXROW(), 0
WAIT "EOF UF_Arrays.prg"
RETURN // UF_Arrays.Main
*-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._
PROCEDURE FileList()
LOCAL aFList := DIRECTORY( "C:\Harbour\*.*" )
LOCAL a1File
FOR EACH a1File IN aFList
? SPACE( 4 ),;
PAD( a1File[ F_NAME ], 13 ),; /* File name */
TRAN( a1File[ F_SIZE ], "999,999,999" ),; /* File size */
a1File[ F_DATE ],; /* File date */
a1File[ F_TIME ],; /* File time */
a1File[ F_ATTR ] /* File attribute */
NEXT
RETURN // FileList()
*-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._
FUNCTION MakUseTable()
LOCAL cTablName := "CUSTOMER.DBF"
LOCAL lRetval, aStru
IF FILE( cTablName )
USE (cTablName)
ELSE
aStru := { { "CUST_ID", "C", 5, 0 },;
{ "CUST_NAME", "C", 10, 0 },;
{ "CUST_SNAM", "C", 10, 0 },;
{ "CUST_FDAT", "D", 8, 0 },;
{ "CUST_ACTV", "L", 1, 0 },;
{ "CUST_BLNCE", "N", 11, 2 } }
*
* 5-th parameter of DBCREATE() is alias -
* if not given then WA is open without alias
* ^^^^^^^^^^^^^
DBCREATE( cTablName, aStru, , .F., "CUSTOMER" )
ENDIF
lRetval := ( ALIAS() == "CUSTOMER" )
RETURN lRetval // MakUseTable()
*-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._
PROCEDURE DispStru()
LOCAL nTotal := 1
IF SELECT() > 0
aStructur := DBSTRUCT()
? SPACE( 4 ), "No: Field Name Type Width Dec"
? SPACE( 4 ), "--- ---------- ---- ----- ---"
AEVAL( aStructur, { | aF1, nFNo | ;
QOUT( SPACE( 4 ),; // Left Marj
PADL( nFNo, 3 ),; // Field No
PADR( aF1[ DBS_NAME ], 11 ),; // Field Name
PADC( aF1[ DBS_TYPE ], 4 ),; // Field Type
PADL( aF1[ DBS_LEN ], 4 ),; // Field Len
PADL( aF1[ DBS_DEC ], 3 )),; // Field Dec
nTotal += aF1[ 3 ] } )
? SPACE( 4 ), "--- ---------- ---- ----- ---"
? SPACE( 4 ), "** Total ** ", TRAN( nTotal, "9,999" )
ELSE
? "Current work area is empty"
ENDIF
RETURN // DispStru()
*-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._.-._