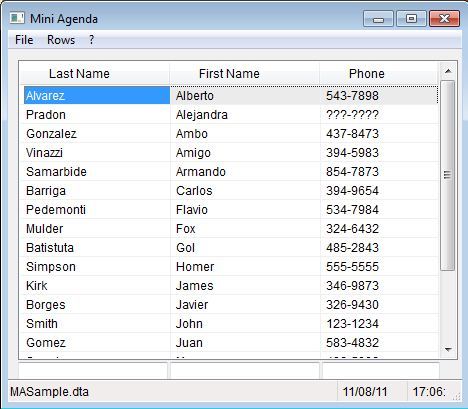
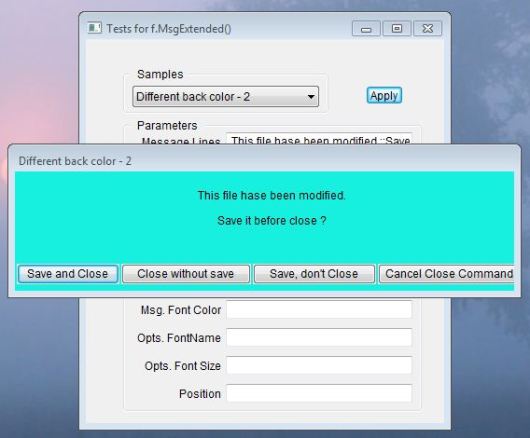
C5 User Interface Commands and Functions
Global Settings :
Modify the date format to include or omit century digits
SET CENTURY on | OFF | <xlToggle>
Define screen colors
SET COLOR | COLOUR TO [[<standard>]
[,<enhanced>] [,<border>] [,<background>]
[,<unselected>]] | (<cColorString>)
Toggle required exit key to terminate GETs
SET CONFIRM on | OFF | <xlToggle>
Toggle console display to the screen
SET CONSOLE ON | off | <xlToggle>
Toggle the screen cursor on or off
SET CURSOR ON | off | <xlToggle>
Set the date format for input and display
SET DATE FORMAT [TO] <cDateFormat>
SET DATE [TO] AMERICAN | ansi | british | french
| german | italian | japan | usa
Set the number of decimal places displayed
SET DECIMALS TO [<nDecimals>]
Toggle or define GET delimiters
SET DELIMITERS on | OFF | <xlToggle>
SET DELIMITERS TO [<cDelimiters> | DEFAULT]
Direct @…SAYs to the screen or printer
SET DEVICE TO SCREEN | printer
Control the interpretation of dates with no century digits
SET EPOCH TO <nYear>
Toggle fixing of the number of decimal digits displayed
SET FIXED on | OFF | <xlToggle>
Toggle asterisk (*) interpretation in SET COLOR
SETBLINK([<lToggle>]) --> lCurrentSetting
Return the current colors and optionally set new colors
SETCOLOR([<cColorString>]) --> cColorString
Set the cursor shape
SETCURSOR([<nCursorShape>]) --> nCurrentSetting
Change display mode to specified number of rows and columns
SETMODE(<nRows>, <nCols>) --> lSuccess
Move the cursor to a new position
SETPOS(<nRow>, <nCol>) --> NIL
User Input :
Empty the keyboard buffer
CLEAR TYPEAHEAD
Extract a character from the keyboard buffer
INKEY( [ <nSeconds> ] ) --> nInkeyCode
Stuff a string into the keyboard buffer
KEYBOARD <cString>
Return the INKEY() value of the last key in the buffer
LASTKEY() --> nInkeyCode
Read the pending key in the keyboard buffer
NEXTKEY() --> nInkeyCode
Set the size of the keyboard buffer
SET TYPEAHEAD TO <nKeyboardSize>
Basic :
Display one or more values to the console
? | ?? [<exp list>]
Draw a box on the screen
@ <nTop>, <nLeft>, <nBottom>, <nRight>
BOX <cBoxString> [COLOR <cColorString>]
Clear a rectangular region of the screen
@ <nTop>, <nLeft> [CLEAR
[TO <nBottom>, <nRight>]]
Display data at a specified screen or printer row and column
@ <nRow>, <nCol>
[SAY <exp>
[PICTURE <cSayPicture>]
[COLOR <cColorString>]]
GET <idVar>
[PICTURE <cGetPicture>]
[COLOR <cColorString>]
[WHEN <lPreExpression>]
[RANGE* <dnLower>, <dnUpper>] |
[VALID <lPostExpression>]
Draw a single or double line box
@ <nTop>, <nLeft>
TO <nBottom>, <nRight> [DOUBLE] [COLOR
<cColorString>]
Place keyboard input into a memory variable
ACCEPT [<expPrompt>] TO <idVar>
Enter the result of an expression into a variable
INPUT [<expPrompt>] TO <idVar>
Display a simple modal dialog box
ALERT( <cMessage>, [<aOptions>] ) --> nChoice
Clear the screen and home the cursor
CLEAR [SCREEN] | CLS
Return the screen cursor column position
COL() --> nCol
COLORSELECT()
Activate attribute in current color settings
COLORSELECT(<nColorIndex>) --> NIL
Write a value to the current device
DEVOUT(<exp>, [<cColorString>]) --> NIL
Write a value to the current device using a picture clause
DEVOUTPICT(<exp>, <cPicture>, [<cColorString>]) --> NIL
Move the cursor or printhead to a new position depending on the
current device
DEVPOS(<nRow>, <nCol>) --> NIL
Begin buffering screen output
DISPBEGIN() --> NIL
Display a box on the screen
DISPBOX(<nTop>, <nLeft>, <nBottom>, <nRight>,
[<cnBoxString>], [<cColorString>]) --> NIL
Return the number of pending DISPEND() requests
DISPCOUNT() --> nDispCount
Display buffered screen updates
DISPEND() --> NIL
Write a value to the display
DISPOUT(<exp>, [<cColorString>]) --> NIL
Write a list of values to the standard error device
OUTERR(<exp list>) --> NIL
Write a list of values to the standard output device
OUTSTD(<exp list>) --> NIL
Display a list of expressions to the console
QOUT([<exp list>]) --> NIL
QQOUT([<exp list>]) --> NIL
Display a saved screen
RESTORE SCREEN [FROM <cScreen>]
Display a saved screen region to a specified location
RESTSCREEN([<nTop>], [<nLeft>],
[<nBottom>], [<nRight>], <cScreen>) --> NIL
Return the screen row position of the cursor
ROW() --> nRow
Save current screen to a buffer or variable
SAVE SCREEN [TO <idVar>]
Save a screen region for later display
SAVESCREEN([<nTop>], [<nLeft>],
[<nBottom>], [<nRight>]) --> cScreen
Scroll a screen region up or down
SCROLL([<nTop>], [<nLeft>],
[<nBottom>], [<nRight>], [<nVert>] [<nHoriz>])
--> NIL
Display or print the contents of a text file
TYPE <xcFile> [TO PRINTER] [TO FILE <xcOutFile>]
Advanced :
Execute a pop-up menu
ACHOICE(<nTop>, <nLeft>, <nBottom>, <nRight>,
<acMenuItems>,
[<alSelectableItems> | <lSelectableItems>],
[<cUserFunction>],
[<nInitialItem>],
[<nWindowRow>]) --> nPosition
Browse records within a window
BROWSE([<nTop>], [<nLeft>],
[<nBottom>], [<nRight>]) --> lSuccess
Browse records in a table format
DBEDIT( [<nTop>], [<nLeft>],
[<nBottom>], <nRight>],
[<acColumns>],
[<cUserFunction>],
[<acColumnSayPictures> | <cColumnSayPicture>],
[<acColumnHeaders> | <cColumnHeader>],
[<acHeadingSeparators> | <cHeadingSeparator>],
[<acColumnSeparators> | <cColumnSeparator>],
[<acFootingSeparators> | <cFootingSeparator>],
[<acColumnFootings> | <cColumnFooting>]) --> NIL
Display records to the console
DISPLAY <exp list>
[TO PRINTER] [TO FILE <xcFile>]
[<scope>] [WHILE <lCondition>]
[FOR <lCondition>] [OFF]
List records to the console
LIST <exp list>
[TO PRINTER] [TO FILE <xcFile>]
[<scope>] [WHILE <lCondition>]
[FOR <lCondition>] [OFF]
Display labels to the console
LABEL FORM <xcLabel>
[TO PRINTER] [TO FILE <xcFile>] [NOCONSOLE]
[<scope>] [WHILE <lCondition>] [FOR <lCondition>]
[SAMPLE]
Display a report to the console
REPORT FORM <xcReport>
[TO PRINTER] [TO FILE <xcFile>] [NOCONSOLE]
[<scope>] [WHILE <lCondition>] [FOR <lCondition>]
[PLAIN | HEADING <cHeading>] [NOEJECT] [SUMMARY]
Display a literal block of text
TEXT [TO PRINTER] [TO FILE <xcFile>]
<text>...
ENDTEXT
GET System :
Standard :
Create a new Get object and display it on the screen
@ <nRow>, <nCol>
[SAY <exp>
[PICTURE <cSayPicture>]
[COLOR <cColorString>]]
GET <idVar>
[PICTURE <cGetPicture>]
[COLOR <cColorString>]
[WHEN <lPreExpression>]
[RANGE* <dnLower>, <dnUpper>] |
[VALID <lPostExpression>]
Release Get objects from the current GetList array
CLEAR GETS
Activate full-screen editing mode using Get objects
READ [SAVE]
Toggle Uparrow and Downarrow as READ exit keys
READEXIT([<lToggle>]) --> lCurrentState
Toggle the current insert mode for READ and MEMOEDIT()
READINSERT([<lToggle>]) --> lCurrentMode
Determine what key was used to terminate a READ
READKEY() --> nReadkeyCode
Activate a full-screen editing mode for a GetList
READMODAL(<aGetList>) --> NIL
Return the current GET/MENU variable name
READVAR() --> cVarName
Toggle Esc as a READ exit key
SET ESCAPE ON | off | <xlToggle>
Activate a format when READ is executed
SET FORMAT TO [<idProcedure>[.<ext>]]
Toggle enhanced display of GETs and PROMPTs
SET INTENSITY ON | off | <xlToggle>
Toggle the message display from READ or MEMOEDIT()
SET SCOREBOARD ON | off | <xlToggle>
Determine if any GET changed during a READ
UPDATED() --> lChange
Getsys.prg Functions :
Return the currently active Get object
GETACTIVE() --> objGet
Apply a key to a Get object from within a Get reader
GETAPPLYKEY(<oGet>, <nKey>) --> NIL
Process SET KEY during Get editing
GETDOSETKEY(<oGet>) --> NIL
Postvalidate the current Get object
GETPOSTVALIDATE(<oGet>) --> lSuccess
Prevalidate a Get object
GETPREVALIDATE(<oGet>) --> lSuccess
Execute standard READ behavior for a Get object
GETREADER(<oGet>) --> NIL
Return, and optionally set, the format file code block
READFORMAT([<bFormat>]) --> bCurrentFormat
Return, and optionally set, the READ terminate flag
READKILL([<lKillRead>]) --> lCurrentSetting
Return, and optionally set, whether a Get changed
READUPDATED([<lChanged>]) --> lCurrentSetting
GET Class :
Class Function :
GetNew() : Create a new Get object
Exported Instance Variables :
badDate : Indicates if the editing buffer contains an invalid date
block : Code block to associate Get with a variable
buffer : Character value that defines the editing buffer
cargo : User-definable variable
changed : Indicates whether the Get:buffer has changed
clear : Indicates whether the editing buffer should be cleared
col : Get column number
colorSpec : Display attributes string
decPos : Decimal point position within the editing buffer
exitState : Means by which the user exited the Get
hasFocus : Indicates whether or not the Get object has input focus
minus : Indicates whether or not a minus sign has been entered
name : Get variable name
original : Character string containing the original value of the Get
picture : PICTURE string
pos : Current cursor position within the editing buffer
postBlock : Code block to validate a newly entered value
preBlock : Code block to decide if editing is permitted
reader : Contains a block to affect READ behavior on a Get object
rejected : Indicates if last insert/overStrike character was rejected
row : Get row number
subscript : Information about array Get objects .
type : Get variable data type
typeOut : Indicates attempt to move the cursor out of editing buffer
Exported Methods :
State Change Methods :
assign() : Assigns the editing buffer contents to the Get variable
colorDisp() : Changes a Get object’s color and then redisplay it
display() : Displays the Get on the screen .
killFocus() : Takes input focus away from the Get object
reset() : Resets the internal state information of the Get
setFocus() : Gives input focus to the Get object
undo() : Sets the Get variable back to Get:original
unTransform() : Converts character value to its original data type
updateBuffer() : Updates the editing buffer and redisplays the Get
varGet() : Returns the current value of the Get variable
varPut() : Sets the Get variable to the passed value
Cursor Movement Methods :
end() : Moves the cursor to the rightmost position
home() : Moves the cursor to the leftmost position
left() : Moves the cursor left one character
right() : Moves the cursor right one character
toDecPos() : Moves the cursor to the immediate right of Get:decPos
wordLeft() : Moves the cursor left one word
wordRight() : Moves the cursor right one word
Editing Methods :
backspace() : Moves the cursor to the left and deletes one character
delete() : Deletes the character under the cursor
delEnd() : Deletes from current cursor position to the end of the Get
delLeft() : Deletes the character to the left of the cursor
delRight() : Deletes the character to the right of the cursor
delWordLeft() : Deletes the word to the left of the cursor
delWordRight() : Deletes the word to the right of the cursor
Text Entry Methods :
insert() : Inserts characters into the editing buffer
overStrike() : Overwrites characters in the editing buffer
Menu System :
Paint a menu item and define a message
@ <nRow>, <nCol> PROMPT <cMenuItem>
[MESSAGE <cExpression>]
Execute a lightbar menu for defined PROMPTs
MENU TO <idVar>
MENUMODAL :
Activate a top bar menu
MENUMODAL(<oTopBar>, <nSelection>, <nMsgRow>,
<nMsgLeft>, <nMsgRight>, <cMsgColor>) --> MenuID
Set the @…PROMPT message line row
SET MESSAGE TO [<nRow> [CENTER | CENTRE]]
Toggle enhanced display of GETs and PROMPTs
SET INTENSITY ON | off | <xlToggle>
Toggle wrapping of the highlights in MENUs
SET WRAP on | OFF | <xlToggle>
Browse Classes :
TBrowse :
Provides objects for browsing table-oriented data.
Description :
A TBrowse object is a general purpose browsing mechanism for table-oriented data. TBrowse objects provide a sophisticated architecture for acquiring, formatting, and displaying data. Data retrieval and file positioning are performed via user-supplied code blocks, allowing a high degree of flexibility and interaction between the browsing mechanism and the underlying data source. The format of individual data items can be precisely controlled via the TBColumn data retrieval code blocks; overall display formatting and attributes can be controlled by sending appropriate messages to the TBrowse object.
A TBrowse object relies on one or more TBColumn objects. A TBColumn object contains the information necessary to define a single column of the browse table (see TBColumn class in this chapter).
During operation, a TBrowse object retrieves data by evaluating code blocks. The data is organized into rows and columns and displayed within a specified rectangular region of the screen. The TBrowse object maintains an internal browse cursor. The data item on which the browse cursor rests is displayed in a highlighted color. (The actual screen cursor is also positioned to the first character of this data item.)
Initially, the browse cursor is placed on the data item at the top left of the browse display. Messages can then be sent to the TBrowse object to navigate the displayed data, causing the browse cursor to move. These messages are normally sent in response to user keystrokes.
New data is automatically retrieved as required by navigation requests. When navigation proceeds past the edge of the visible rectangle, rows or columns beyond that edge are automatically brought into view. When new rows are brought into view, the underlying data source is repositioned by evaluating a code block.
Note: TBrowse objects do not clear the entire window before output during redisplay operations. Part of the window may still be cleared when data from the existing display is scrolled.
Class Functions :
TBrowseNew() :
Create a new TBrowse object
TBrowseNew(<nTop>, <nLeft>, <nBottom>, <nRight>)
--> objTBrowse
Returns a new TBrowse object with the specified coordinate settings. The TBrowse object is created with no columns and no code blocks for data positioning. These must be provided before the TBrowse object can be used.
TBrowseDB() :
Create a new TBrowse object for browsing a database file
TBrowseDB(<nTop>, <nLeft>, <nBottom>, <nRight>)
--> objTBrowse
Returns a new TBrowse object with the specified coordinate settings and default code blocks for data source positioning within database files. The default code blocks execute the GO TOP, GO BOTTOM, and SKIP operations.
Note that TBrowseDB() creates an object with no column objects. To make the TBrowse object usable, you must add a column for each field to be displayed
Exported Instance Variables:
autoLite : Logical value to control highlighting
cargo : User-definable variable
colCount : Number of browse columns
colorSpec : Color table for the TBrowse display
colPos : Current cursor column position
colSep : Column separator character
footSep : Footing separator character
freeze : Number of columns to freeze
goBottomBlock : Code block executed by TBrowse:goBottom()
goTopBlock : Code block executed by TBrowse:goTop()
headSep : Heading separator character
hitBottom : Indicates the end of available data
hitTop : Indicates the beginning of available data
leftVisible : Indicates position of leftmost unfrozen column in display
nBottom : Bottom row number for the TBrowse display
nLeft : Leftmost column for the TBrowse display
nRight : Rightmost column for the TBrowse display
nTop : Top row number for the TBrowse display
rightVisible : Indicates position of rightmost unfrozen column in display
rowCount : Number of visible data rows in the TBrowse display
rowPos : Current cursor row position
skipBlock : Code block used to reposition data source
stable : Indicates if the TBrowse object is stable
Exported Methods:
Cursor Movement Methods :
down() : Moves the cursor down one row
end() : Moves the cursor to the rightmost visible data column
goBottom() : Repositions the data source to the bottom of file
goTop() : Repositions the data source to the top of file
home() : Moves the cursor to the leftmost visible data column
left() : Moves the cursor left one column
pageDown() : Repositions the data source downward
pageUp() : Repositions the data source upward
panEnd() : Moves the cursor to the rightmost data column
panHome() : Moves the cursor to the leftmost visible data column
panLeft() : Pans left without changing the cursor position
panRight() : Pans right without changing the cursor position
right() : Moves the cursor right one column
up() : Moves the cursor up one row
Miscellaneous Methods :
addColumn() : Adds a TBColumn object to the TBrowse object
colorRect() : Alters the color of a rectangular group of cells
colWidth() : Returns the display width of a particular column
configure() : Reconfigures the internal settings of the TBrowse object
deHilite() : Dehighlights the current cell
delColumn() : Delete a column object from a browse
forceStable() : Performs a full stabilization .
getColumn() : Gets a specific TBColumn object
hilite() : Highlights the current cell
insColumn() : Insert a column object in a browse
invalidate() : Forces redraw during next stabilization
refreshAll() : Causes all data to be refreshed during the next stabilize
refreshCurrent() : Causes the current row to be refreshed on next stabilize
setColumn() : Replaces one TBColumn object with another
stabilize() : Performs incremental stabilization
TBColumn :
Provides the column objects TBrowse objects.
Description :
A TBColumn object is a simple object containing the information needed to fully define one data column of a TBrowse object (see the TBrowse reference in this chapter). TBColumn objects have no methods, only exported instance variables.
Class Function :
TBColumnNew() :
Create a new TBColumn object.
TBColumnNew(<cHeading>, <bBlock>) --> objTBColumn
Exported Instance Variables :
block : Code block to retrieve data for the column
cargo : User-definable variable
colorBlock : Code block that determines color of data items
colSep : Column separator character
defColor : Array of numeric indexes into the color table
footing : Column footing
footSep : Footing separator character
heading : Column heading
headSep : Heading separator character
width : Column display width
Example :
This example is a code fragment that creates a TBrowse object and adds some TBColumn objects to it:
USE Customer NEW
//
// Create a new TBrowse object
objBrowse := TBrowseDB(1, 1, 23, 79)
//
// Create some new TBColumn objects and
// add them to the TBrowse object
objBrowse:addColumn(TBColumnNew( "Customer", ;
{|| Customer->Name} ))
objBrowse:addColumn(TBColumnNew( "Address", ;
{|| Customer->Address} ))
objBrowse:addColumn(TBColumnNew( "City", ;
{|| Customer->City} ))
.
. <statements to actually browse the data>
.
CLOSE Customer
For a simple and working sample look at here.